Nevada
|
|
It has been suggested that
Southern Nevada be
merged into this article. (
Discuss)
Proposed since February 2025.
|
|
Nevada
|
|
|---|---|
| Nickname(s):
The Silver State (official);
The Sagebrush State; The Battle Born State |
|
| Motto:
All for Our Country
|
|
| Anthem: "Home Means Nevada" |
|
Location of Nevada within the United States
|
|
| Country | United States |
| Before statehood | Nevada Territory, Utah Territory, Arizona Territory |
| Admitted to the Union | October 31, 1864 (36th) |
| Capital | Carson City |
| Largest city | Las Vegas |
| Largest county or equivalent | Clark |
| Largest metro and urban areas | Las Vegas Valley |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Joe Lombardo (R) |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Stavros Anthony (R) |
| Legislature | Nevada Legislature |
| • Upper house | Senate |
| • Lower house | Assembly |
| Judiciary | Supreme Court of Nevada |
| U.S. senators | Catherine Cortez Masto (D) Jacky Rosen (D) |
| U.S. House delegation | 3 Democrats 1 Republican (list) |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
110,577 sq mi (286,382 km2) |
| • Land | 109,781.18 sq mi (284,332 km2) |
| • Water | 791 sq mi (2,048 km2) 0.72% |
| • Rank | 7th |
| Dimensions | |
| • Length | 492 mi (787 km) |
| • Width | 322 mi (519 km) |
| Elevation | 5,500 ft (1,680 m) |
| Highest elevation | 13,147 ft (4,007.1 m) |
| Lowest elevation | 481 ft (147 m) |
| Population
(2024)
|
|
|
• Total
|
|
| • Rank | 32nd |
| • Density | 26.8/sq mi (10.3/km2) |
| • Rank | 42nd |
| • Median household income | $76,400 (2023)[4] |
| • Income rank | 24th |
| Demonym | Nevadan |
| Language | |
| • Official language | None |
| Time zones | |
| most of state | UTC−08:00 (Pacific) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−07:00 (PDT) |
| West Wendover | UTC−07:00 (Mountain) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−06:00 (MDT) |
| USPS abbreviation |
NV
|
| ISO 3166 code | US-NV |
| Traditional abbreviation | Nev. |
| Latitude | 35° N to 42° N |
| Longitude | 114° 2′ W to 120° W |
| Website | nv |
| List of state symbols | |
|---|---|
| Song | Home Means Nevada |
| Living insignia | |
| Bird | Mountain bluebird (Sialia currucoides) |
| Fish | Lahontan cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii henshawi) |
| Flower | Sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) |
| Grass | Indian Rice Grass |
| Insect | Vivid Dancer Damselfly (Argia vivida) |
| Mammal | Desert bighorn sheep |
| Reptile | Desert tortoise (Gopherus agassizii) |
| Tree | Bristlecone pine, Single-leaf Piñon (Pinus monophylla) |
| Inanimate insignia | |
| Color(s) | Silver, Blue |
| Fossil | Ichthyosaur (Shonisaurus popularis) |
| Gemstone | Virgin Valley Black Fire Opal |
| Mineral | Silver |
| Rock | Sandstone |
| Soil | Orovada series |
| Other | Element: Neon |
| State route marker | |
 |
|
| State quarter | |

Released in 2006
|
|
| Lists of United States state symbols | |
Nevada (/nəˈvædə, -vɑː-/ ⓘ nə-VAD-ə, -VAH-;[5][6] Spanish: [neˈβaða] ⓘ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States.[c] It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, the 32nd-most populous, and the ninth-least densely populated U.S. state. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's population live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area,[7] including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities.[8] Nevada's capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state.
Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle Born State" because it achieved statehood during the Civil War (the words "Battle Born" also appear on its state flag); due to the presidency of Abraham Lincoln, the Union benefited immensely from the support of newly awarded statehood by the infusion of the monetary support of nearly $400 million in silver ore generated at the time by the Comstock Lode.[9] It is also known as the "Sagebrush State", for the native plant of the same name; and as the "Sage-hen State".[10] The state's name means "snowy" in Spanish, referring to Nevada's small overlap with the Sierra Nevada mountain range; however, the rest of Nevada is largely desert and semi-arid, much of it within the Great Basin. Areas south of the Great Basin are within the Mojave Desert, while Lake Tahoe and the Sierra Nevada lie on the western edge. In 2020, 80.1% of the state's land was managed by various jurisdictions of the U.S. federal government, both civilian and military.[11]
Native Americans of the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes inhabit what is now Nevada. The first Europeans to explore the region were Spanish. They called the region Nevada (snowy) because of the snow which covered the mountains in winter, similar to the Sierra Nevada in Spain. The area formed from mostly Alta California and part of Nuevo México's territory within the Viceroyalty of New Spain, which gained independence as Mexico in 1821. The United States annexed the area in 1848 after its victory in the Mexican–American War, and it was incorporated as part of the New Mexico and Utah Territory in 1850. The discovery of silver at the Comstock Lode in 1859 led to a population boom that became an impetus to the creation of Nevada Territory out of western Utah Territory in 1861. Nevada became the 36th state on October 31, 1864, as the second of two states added to the Union during the Civil War (the first being West Virginia).[12]
Nevada is known for its libertarian laws. In 1940, with a population of just over 110,000 people, Nevada was by far the least-populated state, with less than half the population of the next least-populous state, Wyoming.[13] However, legalized gambling and lenient marriage and divorce laws transformed Nevada into a major tourist destination in the 20th century.[14][15] Nevada is the only U.S. state where prostitution is legal, though it is illegal in its most populated regions – Clark County (Las Vegas), Washoe County (Reno) and Carson City (which, as an independent city, is not within the boundaries of any county). The tourism industry remains Nevada's largest employer,[16] with mining continuing as a substantial sector of the economy: Nevada is the fourth-largest producer of gold in the world.[17] It is the driest state. Droughts in Nevada, which are influenced by climate change, have been increasing in frequency and severity,[18] putting a further strain on Nevada's water security.
Etymology
[edit]The name "Nevada" comes from the Spanish adjective nevada ([neˈβaða]), meaning "snow-covered" or "snowy".[19] The state takes its name from the Nevada Territory, which in turn was named for the Sierra Nevada.[20]
Nevadans pronounce the second syllable with the "a" of "apple" (/nəˈvædə/) while some people from outside of the state pronounce it with the "a" of "palm" (/nəˈvɑːdə/).[21] Although the quality, but not the length, of the latter pronunciation is closer to the Spanish pronunciation (Spanish /a/ is open central [ä],[22] whereas American English /ɑː/ varies from back [ɑː] to central [äː]),[23] it is not the pronunciation used by Nevadans. State Assemblyman Harry Mortenson proposed a bill to recognize the alternative pronunciation of Nevada,[24] though the bill was not supported by most legislators and never received a vote. The Nevadan pronunciation is the one used by the state legislature. At one time, the state's official tourism organization, TravelNevada, stylized the name of the state as "Nevăda", with a breve over the a indicating the locally preferred pronunciation,[25] which was also available as a license plate design until 2007.[26]
History
[edit]Indigenous history
[edit]Before the arrival of Europeans, the earliest inhabitants were Indigenous tribes including the Goshute, Southern Paiute, Mohave, and Wašišiw (Washoe people).[27][28]
Before 1861
[edit]
Francisco Garcés was the first European in the area.[29] Nevada was annexed as a part of the Spanish Empire in the northwestern territory of New Spain. Administratively, the area of Nevada was part of the Commandancy General of the Provincias Internas in the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Nevada became a part of Alta California (Upper California) province in 1804 when the Californias were split. With the Mexican War of Independence won in 1821, the province of Alta California became a territory (state) of Mexico, with a small population.
Jedediah Smith entered the Las Vegas Valley in 1827, Peter Skene Ogden traveled the Humboldt River in 1828, and in 1829 a merchant from Nuevo México named Antonio Armijo streamlined travel along the Old Spanish Trail. Chronicling Armijo's route his scout Raphael Rivera was the first to name Las Vegas, in an 1830 report to governor José Antonio Chaves. Following the suggestions by Rivera of a spring, on the published expedition's map, located in the Las Vegas area John C. Frémont set up camp in Las Vegas Springs in 1844. In 1847, Mormons established the State of Deseret, claiming all of Nevada within the Great Basin and the Colorado watershed. They built the first permanent settlement in what is now Nevada, called Mormon Station (now Genoa), in 1851. Additionally, in June 1855, William Bringhurst and 29 other Mormon missionaries built the first permanent structure, a 150-foot square adobe fort, northeast of downtown Las Vegas, converging on the Spanish and Mormon Roads. The fort remained under Salt Lake City's control until the winter of 1858–1859, and the route remained largely under the control of Salt Lake City and Santa Fe tradespersons.
As such, these pioneers laid the foundation for the emergence of the initial settlements between the Sierra Nevadas and Mojave Desert and within the Las Vegas Valley. The enduring influence of New Mexico and Utah culture has since profoundly impacted Nevada's identity, manifesting through New Mexican cuisine and Mormon foodways or New Mexican and Mormon folk musics, into the fabric of Nevada's own cultural landscape.
As a result of the Mexican–American War and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, Mexico permanently lost Alta California in 1848. The new areas acquired by the United States continued to be administered as territories. As part of the Mexican Cession (1848) and the subsequent California Gold Rush that used Emigrant Trails through the area, the state's area evolved first as part of the Utah Territory and New Mexico Territory, then the Nevada Territory (March 2, 1861; named for the Sierra Nevada).[30]

The first discovery of a major U.S. deposit of silver ore occurred in Comstock Lode under Virginia City, Nevada, in 1859.
Separation from Utah Territory
[edit]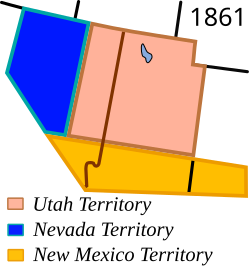
On March 2, 1861, the Nevada Territory separated from the Utah Territory and adopted its current name, shortened from The Sierra Nevada (Spanish for "snow-covered mountain range"). The 1861 southern boundary is commemorated by Nevada Historical Markers 57 and 58 in Lincoln and Nye counties.
Statehood (1864)
[edit]
Eight days before the presidential election of 1864, Nevada became the 36th state in the Union, despite lacking the minimum 60,000 residents that Congress typically required a potential state to have in order to become a state.[31] At the time, Nevada's population was little more than 40,000.[32] Governor Nye was frustrated that previous attempts to send the constitution via overland mail and by sea had failed by October 24, so on October 26 the full text was sent by telegraph at a cost of $4,303.27[33][d] – the most costly telegraph on file at the time for a single dispatch, equivalent to $86,514.04 in 2024. Finally, the response from Washington came on October 31, 1864: "the pain is over, the child is born, Nevada this day was admitted into the Union". Statehood was rushed to the date of October 31 to help ensure Abraham Lincoln's reelection on November 8 and post-Civil War Republican dominance in Congress,[34] as Nevada's mining-based economy tied it to the more industrialized Union. As it turned out, however, Lincoln and the Republicans won the election handily and did not need Nevada's help.
Nevada is one of only two states to significantly expand its borders after admission to the Union, with the other being Missouri, which acquired additional territory in 1837 due to the Platte Purchase. In 1866 another part of the western Utah Territory was added to Nevada in the eastern part of the state, setting the current eastern boundary. Nevada achieved its current southern boundaries on January 18, 1867, when it absorbed the portion of Pah-Ute County in the Arizona Territory west of the Colorado River, essentially all of present-day Nevada south of the 37th parallel. The transfer was prompted by the discovery of gold in the area, and officials thought Nevada would be better able to oversee the expected population boom. This area includes all of what is now Clark County and the southern-most portions of Esmeralda, Lincoln, and Nye counties.[35]

Mining shaped Nevada's economy for many years (see Silver mining in Nevada). When Mark Twain lived in Nevada during the period described in Roughing It, mining had led to an industry of speculation and immense wealth. Both mining and population temporarily declined in the late 19th century. However, the rich silver strike at Tonopah in 1900, followed by strikes in Goldfield and Rhyolite, created a second mining boom in Nevada and Nevada's population.
Gambling and labor
[edit]Unregulated gambling was commonplace in the early Nevada mining towns but was outlawed in 1909 as part of a nationwide anti-gambling crusade. Because of subsequent declines in mining output and the decline of the agricultural sector during the Great Depression, Nevada again legalized gambling on March 19, 1931, with approval from the legislature. Governor Fred B. Balzar's signature enacted the most liberal divorce laws in the country and open gambling. The reforms came just eight days after the federal government presented the $49 million construction contract for Boulder Dam (now Hoover Dam).[37]
Nuclear testing
[edit]The Nevada Test Site, 65 miles (105 km) northwest of the city of Las Vegas, was founded on January 11, 1951, for the testing of nuclear weapons. The site consists of about 1,350 square miles (3,500 km2) of the desert and mountainous terrain. Nuclear testing at the Nevada Test Site began with a 1 kiloton of TNT (4.2 TJ) nuclear bomb dropped on Frenchman Flat on January 27, 1951. The last atmospheric test was conducted on July 17, 1962, and the underground testing of weapons continued until September 23, 1992. The location is known for having the highest concentration of nuclear-detonated weapons in the U.S.
Over 80% of the state's area is owned by the federal government. This is mainly because homesteads were not permitted in large enough sizes to be viable in the arid conditions that prevail throughout desert Nevada. Instead, early settlers would homestead land surrounding a water source, and then graze livestock on the adjacent public land, which is useless for agriculture without access to water (this pattern of ranching still prevails).
2020s
[edit]The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed in Nevada on March 5, 2020. Because of concerns about coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Nevada governor Steve Sisolak declared a state of emergency on March 12, 2020. Four days later, Nevada reported its first death. On March 17, 2020, Sisolak ordered the closure of non-essential businesses in the state to help prevent the spread of the coronavirus.
Various protests were held against Sisolak's shutdown order beginning in April 2020. Nevada launched the first phase of its reopening on May 9, 2020. Restaurants, retailers, outdoor malls, and hair salons were among the businesses allowed to reopen, but with precautions in place, such as limiting occupancy to 50 percent. A second phase went into effect on May 29, 2020. It allowed for the reopening of state parks and businesses such as bars, gyms, and movie theaters. Casinos began reopening on June 4, 2020.
Geography
[edit]|
This article
needs additional citations for verification.
(December 2021)
|



Nevada is almost entirely within the Basin and Range Province and is broken up by many north–south mountain ranges. Most of these ranges have endorheic valleys between them.
Much of the northern part of the state is within the Great Basin, a mild desert that experiences hot temperatures in the summer and cold temperatures in the winter. Occasionally, moisture from the Arizona Monsoon will cause summer thunderstorms; Pacific storms may blanket the area with snow. The state's highest recorded temperature was 125 °F (52 °C) in Laughlin (elevation of 605 feet or 184 meters) on June 29, 1994.[38] The coldest recorded temperature was −52 °F (−47 °C) set in San Jacinto in 1972, in the northeastern portion of the state.[38]
The Humboldt River crosses the state from east to west across the northern part of the state, draining into the Humboldt Sink near Lovelock. Several rivers drain from the Sierra Nevada eastward, including the Walker, Truckee, and Carson rivers. All of these rivers are endorheic basins, ending in Walker Lake, Pyramid Lake, and the Carson Sink, respectively. However, not all of Nevada is within the Great Basin. Tributaries of the Snake River drain the far north, while the Colorado River, which also forms much of the boundary with Arizona, drains much of southern Nevada.
The mountain ranges, some of which have peaks above 13,000 feet (4,000 m), harbor lush forests high above desert plains, creating sky islands for endemic species. The valleys are often no lower in elevation than 3,000 feet (910 m), while some in central Nevada are above 6,000 feet (1,800 m).

The southern third of the state, where the Las Vegas area is situated, is within the Mojave Desert. The area receives less rain in the winter but is closer to the Arizona Monsoon in the summer. The terrain is also lower, mostly below 4,000 feet (1,200 m), creating conditions for hot summer days and cool to chilly winter nights.
Nevada and California have by far the longest diagonal line (in respect to the cardinal directions) as a state boundary at just over 400 miles (640 km). This line begins in Lake Tahoe nearly 4 miles (6.4 km) offshore (in the direction of the boundary), and continues to the Colorado River where the Nevada, California, and Arizona boundaries merge 12 miles (19 km) southwest of the Laughlin Bridge.
The largest mountain range in the southern portion of the state is the Spring Mountain Range, just west of Las Vegas. The state's lowest point is along the Colorado River, south of Laughlin.
Nevada has 172 mountain summits with 2,000 feet (610 m) of prominence. Nevada ranks second, after Alaska, for the greatest number of mountains in the United States, followed by California, Montana, and Washington.[39]
Climate
[edit]
Nevada is the driest state in the United States.[40] It is made up of mostly desert and semi-arid climate regions, and, with the exception of the Las Vegas Valley, the average summer diurnal temperature range approaches 40 °F (22 °C) in much of the state. While winters in northern Nevada are long and fairly cold, the winter season in the southern part of the state tends to be of short duration and mild. Most parts of Nevada receive scarce precipitation during the year. The most rain that falls in the state falls on the east and northeast slopes of the Sierra Nevada.
The average annual rainfall per year is about 7 inches (180 mm); the wettest parts get around 40 inches (1,000 mm). Nevada's highest recorded temperature is 125 °F (52 °C) at Laughlin on June 29, 1994, and the lowest recorded temperature is −50 °F (−46 °C) at San Jacinto on January 8, 1937. Nevada's 125 °F (52 °C) reading is the third highest statewide record high temperature of a U.S. state, just behind Arizona's 128 °F (53 °C) reading and California's 134 °F (57 °C) reading.
| Location | July (°F) | July (°C) | December (°F) | December (°C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | |
| Las Vegas | 106 | 81 | 41 | 27 | 56 | 38 | 13 | 3 |
| Reno | 92 | 57 | 33 | 14 | 45 | 25 | 7 | –4 |
| Carson City | 89 | 52 | 32 | 11 | 45 | 22 | 7 | –5 |
| Elko | 90 | 50 | 32 | 10 | 37 | 14 | 2 | –9 |
| Fallon | 92 | 54 | 33 | 12 | 45 | 19 | 7 | –7 |
| Winnemucca | 93 | 52 | 34 | 11 | 41 | 17 | 5 | –8 |
| Laughlin | 112 | 80 | 44 | 27 | 65 | 43 | 18 | 6 |
Flora and fauna
[edit]The vegetation of Nevada is diverse and differs by state area. Nevada contains six biotic zones: alpine, sub-alpine, ponderosa pine, pinion-juniper, sagebrush and creosotebush.[42]
Counties
[edit]

Nevada is divided into political jurisdictions designated as counties. Carson City is officially a consolidated municipality, meaning it legally functions as both a city and a county. As of 1919, there were 17 counties in the state, ranging from 146 to 18,159 square miles (380 to 47,030 km2).
Lake County, one of the original nine counties formed in 1861, was renamed Roop County in 1862. Part of the county became Lassen County, California, in 1864, resolving border uncertainty. In 1883, Washoe County annexed the portion that remained in Nevada.[43]
In 1969, Ormsby County was dissolved and the Consolidated Municipality of Carson City was created by the Legislature in its place coterminous with the old boundaries of Ormsby County.
Bullfrog County was formed in 1987 from part of Nye County. After the creation was declared unconstitutional, the county was abolished in 1989.[43]
Humboldt County was designated as a county in 1856 by Utah Territorial Legislature and again in 1861 by the new Nevada Legislature.
Clark County is the most populous county in Nevada, accounting for nearly three-quarters of its residents. Las Vegas, Nevada's most populous city, has been the county seat since the county was created in 1909 from a portion of Lincoln County, Nevada. Before that, it was a part of Arizona Territory. Clark County attracts numerous tourists: An estimated 44 million people visited Clark County in 2014.[44]
Washoe County is the second-most populous county of Nevada. Its county seat is Reno. Washoe County includes the Reno–Sparks metropolitan area.
Lyon County is the third most populous county. It was one of the nine original counties created in 1861. It was named after Nathaniel Lyon, the first Union General to be killed in the Civil War. Its current county seat is Yerington. Its first county seat was established at Dayton on November 29, 1861.[45]
| County name | County seat | Year founded | 2022 population[46] | Percent of total | Area | Percent of total | Population density | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sq mi | km2 | per sq mi | per km2 | ||||||
| Carson City | Carson City | 1861 | 58,130 | 1.83 % | 157 | 410 | 0.14 % | 370.25 | 142.95 |
| Churchill | Fallon | 1861 | 25,843 | 0.81 % | 5,024 | 13,010 | 4.54 % | 5.14 | 1.98 |
| Clark | Las Vegas | 1908 | 2,322,985 | 73.10 % | 8,061 | 20,880 | 7.29 % | 288.18 | 111.27 |
| Douglas | Minden | 1861 | 49,628 | 1.56 % | 738 | 1,910 | 0.67 % | 67.25 | 25.97 |
| Elko | Elko | 1869 | 54,046 | 1.70 % | 17,203 | 44,560 | 15.56 % | 3.14 | 1.21 |
| Esmeralda | Goldfield | 1861 | 744 | 0.02 % | 3,589 | 9,300 | 3.25 % | 0.21 | 0.081 |
| Eureka | Eureka | 1869 | 1,863 | 0.06 % | 4,180 | 10,800 | 3.78 % | 0.45 | 0.17 |
| Humboldt | Winnemucca | 1856/1861 | 17,272 | 0.54 % | 9,658 | 25,010 | 8.73 % | 1.79 | 0.69 |
| Lander | Battle Mountain | 1861 | 5,766 | 0.18 % | 5,519 | 14,290 | 4.99 % | 1.04 | 0.40 |
| Lincoln | Pioche | 1867 | 4,482 | 0.14 % | 10,637 | 27,550 | 9.62 % | 0.42 | 0.16 |
| Lyon | Yerington | 1861 | 61,585 | 1.94 % | 2,024 | 5,240 | 1.83 % | 30.43 | 11.75 |
| Mineral | Hawthorne | 1911 | 4,525 | 0.14 % | 3,813 | 9,880 | 3.45 % | 1.19 | 0.46 |
| Nye | Tonopah | 1864 | 54,738 | 1.72 % | 18,199 | 47,140 | 16.46 % | 3.01 | 1.16 |
| Pershing | Lovelock | 1919 | 6,462 | 0.20 % | 6,067 | 15,710 | 5.49 % | 1.07 | 0.41 |
| Storey | Virginia City | 1861 | 4,170 | 0.13 % | 264 | 680 | 0.24 % | 15.80 | 6.10 |
| Washoe | Reno | 1861 | 496,745 | 15.63 % | 6,542 | 16,940 | 5.92 % | 75.93 | 29.32 |
| White Pine | Ely | 1869 | 8,788 | 0.28 % | 8,897 | 23,040 | 8.05 % | 0.99 | 0.38 |
| Totals | Counties: 17 | 3,177,772 | 110,572 | 286,380 | 28.74 | 11.10 | |||
Settlements
[edit]|
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | County | Pop. | ||||||
 Las Vegas  Henderson |
1 | Las Vegas | Clark | 641,903 |  Reno North Las Vegas |
||||
| 2 | Henderson | Clark | 317,610 | ||||||
| 3 | Reno | Washoe | 264,165 | ||||||
| 4 | North Las Vegas | Clark | 262,527 | ||||||
| 5 | Enterprise | Clark | 221,831 | ||||||
| 6 | Spring Valley | Clark | 215,597 | ||||||
| 7 | Sunrise Manor | Clark | 205,618 | ||||||
| 8 | Paradise | Clark | 191,238 | ||||||
| 9 | Sparks | Washoe | 108,445 | ||||||
| 10 | Carson City | Carson City | 58,639 | ||||||
Parks and recreation areas
[edit]




Recreation areas maintained by the federal government
[edit]Northern Nevada
[edit]- Basin and Range National Monument
- Black Rock Desert-High Rock Canyon Emigrant Trails National Conservation Area
- California National Historic Trail
- Great Basin National Park
- Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest
- Lake Tahoe Basin Management Unit
- Pony Express National Historic Trail
- Sheldon National Wildlife Refuge
Southern Nevada
[edit]- Ash Meadows National Wildlife Preserve
- Avi Kwa Ame National Monument
- Basin and Range National Monument
- Bootleg Canyon Mountain Bike Park
- Death Valley National Park
- Desert National Wildlife Refuge
- Gold Butte National Monument
- Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest
- Inyo National Forest
- Lake Mead National Recreation Area
- Moapa Valley National Wildlife Refuge
- Mount Charleston and the Mount Charleston Wilderness
- Old Spanish National Historic Trail
- Pahranagat National Wildlife Refuge
- Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area
- Sloan Canyon National Conservation Area
- Spring Mountains and the Spring Mountains National Recreation Area
- Tule Springs Fossil Beds National Monument
Wilderness
[edit]There are 68 designated wilderness areas in Nevada, protecting some 6,579,014 acres (2,662,433 ha) under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service, U.S. Forest Service, and Bureau of Land Management.[48]
State parks
[edit]The Nevada state parks comprise protected areas managed by the state of Nevada, including state parks, state historic sites, and state recreation areas. There are 24 state park units, including Van Sickle Bi-State Park which opened in July 2011 and is operated in partnership with the adjacent state of California.[49]
Demographics
[edit]Population
[edit]
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1860 | 6,857 | — | |
| 1870 | 42,941 | 526.2% | |
| 1880 | 62,266 | 45.0% | |
| 1890 | 47,355 | −23.9% | |
| 1900 | 42,335 | −10.6% | |
| 1910 | 81,875 | 93.4% | |
| 1920 | 77,407 | −5.5% | |
| 1930 | 91,058 | 17.6% | |
| 1940 | 110,247 | 21.1% | |
| 1950 | 160,083 | 45.2% | |
| 1960 | 285,278 | 78.2% | |
| 1970 | 488,738 | 71.3% | |
| 1980 | 800,493 | 63.8% | |
| 1990 | 1,201,833 | 50.1% | |
| 2000 | 1,998,257 | 66.3% | |
| 2010 | 2,700,551 | 35.1% | |
| 2020 | 3,104,614 | 15.0% | |
| 2024 (est.) | 3,267,467 | 5.2% | |
| Source: 1910–2020[50] | |||

The United States Census Bureau determined Nevada had a population of 3,104,614 at the 2020 U.S. census. In 2022, the estimated population of Nevada was 3,177,772, an increase of 73,158 residents (2.36%) since the 2020 census.[51] Nevada had the highest percentage growth in population from 2017 to 2018. At the 2020 census, 6.0% of the state's population were reported as under 5, 22.5% were under 18, and 16.1% were 65 or older. Females made up about 49.8% of the population. 19.1% of the population was reported as foreign-born.
Since the 2020 census, the population of Nevada had a natural increase of 2,374 (the net difference between 42,076 births and 39,702 deaths); and an increase due to net migration of 36,605 (of which 34,280 was due to domestic and 2,325 was due to international migration).[52]
The center of population of Nevada is in southern Nye County.[53] In this county, the unincorporated town of Pahrump, 60 miles (97 km) west of Las Vegas on the California state line, has grown very rapidly from 1980 to 2020. At the 2020 census, the town had 44,738 residents.[54] Las Vegas grew from a gulch of 100 people in 1900 to 10,000 by 1950 to 100,000 by 1970, and was America's fastest-growing city and metropolitan area from 1960 to 2000.
From about the 1940s until 2003, Nevada was the fastest-growing state in the U.S. percentage-wise. Between 1990 and 2000, Nevada's population increased by 66%, while the nation's population increased by 13%. More than two-thirds of the population live in Clark County, which is coextensive with the Las Vegas metropolitan area. Thus, in terms of population, Nevada is one of the most centralized states in the nation.
Henderson and North Las Vegas are among the top 20 fastest-growing U.S. cities with populations over 100,000. The rural community of Mesquite 65 miles (105 km) northeast of Las Vegas was an example of micropolitan growth in the 1990s and 2000s. Other desert towns like Indian Springs and Searchlight on the outskirts of Las Vegas have seen some growth as well.
Since 1950, the rate of population born in Nevada has never peaked above 27 percent, the lowest rate of all states. In 2012, only 25% of Nevadans were born in Nevada.[55]
According to HUD's 2022 Annual Homeless Assessment Report, there were an estimated 7,618 homeless people in Nevada.[56][57]
Race and ethnicity
[edit]| Race / Ethnicity | Pop 2000[58] | Pop 2010[59] | Pop 2020[60] | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 1,303,001 | 1,462,081 | 1,425,952 | 65.21% | 54.14% | 45.93% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 131,509 | 208,058 | 291,960 | 6.58% | 7.70% | 9.40% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 21,397 | 23,536 | 23,392 | 1.07% | 0.87% | 0.75% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 88,593 | 191,047 | 265,991 | 4.43% | 7.07% | 8.57% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 7,769 | 15,456 | 22,970 | 0.39% | 0.57% | 0.74% |
| Some Other Race alone (NH) | 2,787 | 4,740 | 17,171 | 0.14% | 0.18% | 0.55% |
| Mixed Race/Multi-Racial (NH) | 49,231 | 79,132 | 166,921 | 2.46% | 2.93% | 5.38% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 393,970 | 716,501 | 890,257 | 19.72% | 26.53% | 28.68% |
| Total | 1,998,257 | 2,700,551 | 3,104,614 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Race and Ethnicity[61] | Alone | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White (non-Hispanic) | 45.9% |
|
50.6% |
|
| Hispanic or Latino[e] | — | 28.7% |
|
|
| Multiracial | — | 14.0% |
|
|
| African American (non-Hispanic) | 9.4% |
|
11.1% |
|
| Asian | 8.6% |
|
10.7% |
|
| Native American | 0.8% |
|
2.1% |
|
| Pacific Islander | 0.7% |
|
1.5% |
|
| Other | 0.6% |
|
1.4% |
|
According to the 2022 American Community Survey, 30.3% of Nevada's population were of Hispanic or Latino origin (of any race): Mexican (22%), Cuban (1.5%), Salvadoran (1.5%), Puerto Rican (1%), and other Hispanic or Latino origin (4.3%).[62] The largest European ancestry groups were: German (8.9%), English (8.1%), Irish (7.2%), and Italian (4.8%).[63] The largest Asian ancestry groups in the state were Filipino (6.4%) and Chinese (1.9%).[64]

-
Non-Hispanic White 30–40%50–60%60–70%70–80%80–90%
In 1980, non-Hispanic whites made up 83.2% of the state's population.[65]
| Racial composition | 1970[65] | 1980 | 1990[65] | 2000[66] | 2010[67] | 2020[68] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 91.7% | 87.5% | 84.3% | 75.2% | 66.2% | 51.2% |
| Black | 5.7% | 6.4% | 6.6% | 6.8% | 8.1% | 9.8% |
| Asian | 0.7% | 1.8% | 3.2% | 4.5% | 7.2% | 8.8% |
| Native | 1.6% | 1.7% | 1.6% | 1.3% | 1.2% | 1.4% |
| Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander |
– | – | – | 0.4% | 0.6% | 0.8% |
| Other race | 0.3% | 2.7% | 4.4% | 8.0% | 12.0% | 14.0% |
| Two or more races | – | – | – | 3.8% | 4.7% | 14.0% |
| Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 5.6% | 6.7% | 10.4% | 19.7% | 26.5% | 28.7% |
| Non-Hispanic white | 86.7% | 83.2% | 78.7% | 65.2% | 54.1% | 45.9% |
As of 2011, 63.6% of Nevada's population younger than age 1 were minorities.[69] Las Vegas is a majority-minority city. According to the United States Census Bureau estimates, as of July 1, 2018, non-Hispanic Whites made up 48.7% of Nevada's population.[70]
In Douglas, Mineral, and Pershing counties, a plurality of residents are of Mexican ancestry. In Nye County and Humboldt County, residents are mostly of German ancestry; Washoe County has many Irish Americans. Americans of English descent form pluralities in Lincoln County, Churchill County, Lyon County, White Pine County, and Eureka County.
Asian Americans have lived in the state since at least the 1850s, when the California gold rush brought thousands of Chinese miners to Washoe County. They were followed by a few hundred Japanese farmworkers in the late 19th century. By the late 20th century, many immigrants from China, Japan, Korea, the Philippines, Bangladesh, India, and Vietnam came to the Las Vegas metropolitan area. The city now has a significant Asian American community, with a mostly Chinese and Taiwanese area known as "Chinatown" west of I-15 on Spring Mountain Road. Filipino Americans form the largest Asian American group in the state, with a population of more than 202,000. They comprise 59.8% of the Asian American population in Nevada and constitute about 6.4% of the entire state's population.[71]
Mining booms drew many Greek and Eastern European immigrants to Nevada.[72] In the early twentieth century, Greeks, Slavs, Danes, Japanese, Italians, and Basques poured into Nevada.[73] Chileans were found in the state as early as 1870.[74] During the mid-1800s, a significant number of European immigrants, mainly from Ireland, England and Germany, arrived in the state with the intention of capitalizing on the thriving mining sector in the region.[75]
Native American tribes in Nevada are the Northern and Southern Paiute, Western Shoshone, Goshute, Hualapai, Washoe, and Ute tribes.[76]
Whites remain the largest racial or ethnic group in Nevada.[77] Hispanics are the fastest growing ethnic group in Nevada.[78] There is a growing Mexican and Central American population in Nevada. Many of Nevada's Latino immigrants are from Mexico, Guatemala and El Salvador.[79] Nevada also has a growing multiracial population.[80]
The top countries of origin for immigrants in Nevada were Mexico (39.5 percent of immigrants), the Philippines (14.3 percent), El Salvador (5.2 percent), China (3.1 percent), and Cuba (3 percent).[81]
The majority of people in Nevada are of white (European) ancestry. A small portion trace their ancestry to Basque people recruited as sheepherders. Hispanics in Nevada are mainly of Mexican and Cuban heritage. Latinos comprise about one-fourth of Nevada's residents and are concentrated in the southeast in Nevada. African Americans live mainly in the Las Vegas and Reno area and constitute less than one-tenth of the population. Native Americans of the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes live on several reservations in the state and make up a small fraction of Nevada's population.[82]
The most common ancestries in Nevada include Mexican, German, Irish, English, Italian and Asian.[83]
Nevada is the third most diverse state in the country, behind only Hawaii and California.[84][85]
- Birth data
Note: Births within the table do not add up, due to Hispanics being counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.
| Race | 2013[86] | 2014[87] | 2015[88] | 2016[89] | 2017[90] | 2018[91] | 2019[92] | 2020[93] | 2021[94] | 2022[95] | 2023[96] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 14,951 (42.7%) | 15,151 (42.2%) | 14,937 (41.2%) | 13,918 (38.4%) | 13,171 (36.8%) | 13,021 (36.5%) | 12,479 (35.6%) | 11,602 (34.5%) | 11,800 (35.0%) | 10,961 (33.0%) | 10,448 (32.9%) |
| Black | 4,215 (12.0%) | 4,603 (12.8%) | 4,803 (13.2%) | 4,205 (11.6%) | 4,471 (12.5%) | 4,564 (12.8%) | 4,514 (12.9%) | 4,533 (13.5%) | 4,457 (13.2%) | 4,334 (13.1%) | 4,093 (12.9%) |
| Asian | 3,097 (8.8%) | 3,145 (8.8%) | 3,337 (9.2%) | 2,666 (7.3%) | 2,685 (7.5%) | 2,613 (7.3%) | 2,587 (7.4%) | 2,467 (7.3%) | 2,372 (7.0%) | 2,548 (7.7%) | 2,461 (7.7%) |
| Pacific Islander | ... | ... | ... | 308 (0.8%) | 322 (0.9%) | 340 (1.0%) | 372 (1.1%) | 358 (1.1%) | 331 (1.0%) | 358 (1.1%) | 325 (1.0%) |
| American Indian | 425 (1.2%) | 475 (1.3%) | 510 (1.4%) | 303 (0.8%) | 305 (0.9%) | 280 (0.8%) | 277 (0.8%) | 234 (0.7%) | 239 (0.7%) | 218 (0.7%) | 208 (0.6%) |
| Hispanic (any race) | 12,718 (36.3%) | 13,006 (36.3%) | 13,225 (36.4%) | 13,391 (36.9%) | 13,176 (36.8%) | 13,307 (37.3%) | 13,238 (37.7%) | 12,763 (37.9%) | 12,842 (38.1%) | 13,019 (39.2%) | 12,631 (39.7%) |
| Total | 35,030 (100%) | 35,861 (100%) | 36,298 (100%) | 36,260 (100%) | 35,756 (100%) | 35,682 (100%) | 35,072 (100%) | 33,653 (100%) | 33,686 (100%) | 33,193 (100%) | 31,794 (100%) |
- Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one Hispanic group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.



A small percentage of Nevada's population lives in rural areas. The culture of these places differs significantly from major metropolitan areas. People in these rural counties tend to be native Nevada residents, unlike in the Las Vegas and Reno areas, where the vast majority of the population was born in another state. The rural population is also less diverse in terms of race and ethnicity. Mining plays an important role in the economies of the rural counties, with tourism being less prominent.[97] Ranching also has a long tradition in rural Nevada.[98]
Locations by per capita income
[edit]| Rank | Place | Per capita income | County | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Crystal Bay | $180,334 | Washoe | |
| 2 | Glenbrook | $102,963 | Douglas | |
| 3 | Zephyr Cove | $94,920 | Douglas | |
| 4 | Genoa | $86,185 | Douglas | |
| 5 | Incline Village | $74,294 | Washoe | |
| 6 | Kingsbury | $68,215 | Douglas | |
| 7 | Round Hill Village | $67,659 | Douglas | |
| 8 | East Valley | $67,169 | Douglas | |
| 9 | Summerlin South | $65,633 | Clark | |
| 10 | Mount Charleston | $57,583 | Clark | |
Religion
[edit]- Unaffiliated (40%)
- Protestantism (25%)
- Catholicism (21%)
- Mormonism (5%)
- New Age (4%)
- Jehovah's Witnesses (2%)
- Judaism (2%)
- Hinduism (1%)
Church attendance in Nevada is among the lowest of all U.S. states. In a 2009 Gallup poll only 30% of Nevadans said they attended church weekly or almost weekly, compared to 42% of all Americans (only four states were found to have a lower attendance rate than Nevada's).[100] In 2020, the Public Religion Research Institute determined 67% of the population were Christian,[101] reflecting a 1% increase in religiosity from 2014's separate Pew study.[102]
Major religious affiliations of the people of Nevada were, according to the Pew Research Center in 2014: Protestant 35%, Irreligious 28%, Roman Catholic 25%, Latter-day Saints 4%, Jewish 2%, Hindu less than 1%, Buddhist 0.5% and Muslim around 0.2%. Parts of Nevada (in the eastern parts of the state) are situated in the Mormon Corridor.
The largest denominations by number of adherents in 2010 were the Roman Catholic Church with 451,070; The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 175,149; and the Southern Baptist Convention with 45,535; Buddhist congregations 14,727; Baháʼí Faith 1,723; and Muslim 1,700.[103]
Languages
[edit]The most common non-English languages spoken in Nevada are Spanish, Tagalog and Chinese.[104] Indigenous languages of Nevada include Northern Paiute, the Southern Paiute, Shoshone, and Washo.[105]
The top seven languages spoken in Nevada according to the U.S. Census data are Spanish, Tagalog, Chinese, Vietnamese, Korean, Amharic, Arabic, and Thai.[106]
Native American tribes
[edit]Historically what is now Nevada has been inhabited mainly by the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe.[107]
The largest Native American tribes in Nevada according to the 2010 census are listed in the table below:[108]
| Tribal grouping | American Indian and Alaska Native alone |
AIAN in combination with one or more other races |
Total AIAN alone or in any combination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total AIAN population | 32062 | 23883 | 55945 |
| Cherokee | 1824 | 4376 | 6200 |
| Paiute | 4182 | 677 | 4859 |
| Navajo | 1926 | 671 | 2597 |
| Paiute-Shoshone | 2118 | 170 | 2288 |
| Mexican American Indian | 1222 | 708 | 1930 |
| Shoshone | 1388 | 400 | 1788 |
| Choctaw | 597 | 872 | 1469 |
| Apache | 719 | 690 | 1409 |
| Sioux | 702 | 626 | 1328 |
| Blackfeet | 284 | 877 | 1161 |
| Te-Moak Tribes of Western Shoshone | 1011 | 118 | 1129 |
| Washoe | 815 | 130 | 945 |
| Ojibwe | 494 | 338 | 832 |
| Reno-Sparks Indian Colony | 579 | 13 | 592 |
| Iroquois | 228 | 283 | 511 |
| Tribe not specified | 9413 | 10117 | 19530 |
Economy
[edit]





The economy of Nevada is tied to tourism (especially entertainment and gambling related), mining, and cattle ranching. Nevada's industrial outputs are tourism, entertainment, mining, machinery, printing and publishing, food processing, and electric equipment. The Bureau of Economic Analysis[110][111] estimates Nevada's total state product in 2018 was $170 billion.[112] The state's per capita personal income in 2020 was $53,635, ranking 31st in the nation.[113] Nevada's state debt in 2012 was calculated to be $7.5 billion, or $3,100 per taxpayer.[114] As of May 2021, the state's unemployment rate was 7.8%.[115]
Mining
[edit]In portions of the state outside of the Las Vegas and Reno metropolitan areas mining plays a major economic role. By value, gold is by far the most important mineral mined. In 2022, 4,040,000 troy ounces (126 t) of gold worth $7.3 billion were mined in Nevada, and the state accounted for 4% of world gold production. Other minerals mined in Nevada include construction aggregates, copper, gypsum, diatomite and lithium.[116][117] Despite its rich deposits, the cost of mining in Nevada is generally high, and output is very sensitive to world commodity prices.
Cattle ranching
[edit]Cattle ranching is a major economic activity in rural Nevada.[118] Nevada's agricultural outputs are cattle, hay, alfalfa, dairy products, onions, and potatoes. In 2020, there were an estimated 438,511 head of cattle and 71,699 head of sheep in Nevada.[119] Most of these animals forage on rangeland in the summer, with supplemental feed in the winter. Calves are generally shipped to out-of-state feedlots in the fall to be fattened for the market. Over 90% of Nevada's 653,891 acres (264,620 ha) of cropland is used to grow hay, mostly alfalfa, for livestock feed.[119]
Largest employers
[edit]The largest employers in the state, as of the first fiscal quarter of 2011, are the following, according to the Nevada Department of Employment, Training and Rehabilitation:[120]
Infrastructure
[edit]Transportation
[edit]

Amtrak's California Zephyr train uses the Union Pacific's original transcontinental railroad line in daily service from Chicago to Emeryville, California, serving Elko, Winnemucca, and Reno. Las Vegas has had no passenger train service since Amtrak's Desert Wind was discontinued in 1997. Amtrak Thruway buses provide connecting service from Las Vegas to trains at Needles, California, Los Angeles, and Bakersfield, California; and from Stateline, Nevada, to Sacramento, California. There have been a number of proposals to re-introduce service to either Los Angeles or Southern California with the privately run Brightline West having begun construction in 2024.
The Union Pacific Railroad has some railroads in the north and south of Nevada. Greyhound Lines provide some bus service to the state.
Interstate 15 (I-15) passes through the southern tip of the state, serving Las Vegas and other communities. I-215 and I-515 also serve the Las Vegas metropolitan area. I-80 crosses through the northern part of Nevada, roughly following the path of the Humboldt River from Utah in the east and the Truckee River westward through Reno into California. It has a spur route, I-580. Nevada also is served by several U.S. highways: US 6, US 50, US 93, US 95 and US 395. There are also 189 Nevada state routes. Many of Nevada's counties have a system of county routes as well, though many are not signed or paved in rural areas. Nevada is one of a few states in the U.S. that do not have a continuous interstate highway linking its two major population centers – the road connection between the Las Vegas and Reno areas is a combination of several different Interstate and U.S. highways. The Interstate 11 proposed routing may eventually remedy this.[121]
The state is one of just a few in the country to allow semi-trailer trucks with three trailers – what might be called a "road train" in Australia. But American versions are usually smaller, in part because they must ascend and descend some fairly steep mountain passes.
RTC Transit is the public transit system in the Las Vegas metropolitan area. The agency is the largest transit agency in the state and operates a network of bus service across the Las Vegas Valley, including the use of The Deuce, double-decker buses, on the Las Vegas Strip and several outlying routes. RTC RIDE operates a system of local transit bus service throughout the Reno-Sparks metropolitan area. Other transit systems in the state include Carson City's JAC. Most other counties in the state do not have public transportation at all.
Additionally, a 4-mile (6.4 km) monorail system provides public transportation in the Las Vegas area. The Las Vegas Monorail line services several casino properties and the Las Vegas Convention Center on the east side of the Las Vegas Strip, running near Paradise Road, with a possible future extension to Harry Reid International Airport. Several hotels also run their own monorail lines between each other, which are typically several blocks in length.
Harry Reid International Airport in Las Vegas is the busiest airport serving Nevada. The Reno-Tahoe International Airport (formerly known as the Reno Cannon International Airport) is the other major airport in the state.
Energy
[edit]| External image | |
|---|---|
Nevada has had a thriving solar energy sector. An independent study in 2013 concluded that solar users created a $36 million net benefit. However, in December 2015, the Public Utility Commission let the state's only power company, NV Energy, charge higher rates and fees to solar panel users, leading to an immediate collapse of rooftop solar panel use.[122]
In December 1987, Congress amended the Nuclear Waste Policy Act to designate Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository as the only site to be characterized as a permanent repository for all of the nation's highly radioactive waste.[123]
Affordable housing
[edit]In 2018, the National Low Income Housing Coalition calculated the discrepancy between available affordable housing units and renters who earn below the poverty line. In Nevada, only 15 affordable rental homes are available per 100 extremely low income (ELI) households.[124] The shortage extended to a deficit in supply of 71,358 affordable rental homes. This was the largest discrepancy of any state. The most notable catalyst for this shortage was the Great Recession and housing crisis of 2007 and 2008. Since then, housing prices have increased while demand has increased, and supply has struggled to match the increase in demand. In addition, low-income service workers were slowly being pushed out by an influx of tech professionals. In Nevada there is essentially a standard of six-figure income to affordably rent a single-family home.[125] Considering the average salary in Nevada, $54,842 per year, this standard is on average, unaffordable.[126] The disproportionate cost of housing compared to average salary has led to 112,872 renters to be paying more than half of their yearly income towards housing.[127]
The definition of an affordable home is "one that a household can obtain for 30 percent or less of its annual income". So, there is clearly a long way to go in order to close the gap between housing prices and relative income in the state. Renters are looking for solutions to still be able to live in the state in a way that their income can support. As a result, single adults are being forced to split rent with other renters or move residences to farther outside metro areas. One solution being offered is to increase the supply of higher income positions within the state to make things more affordable. However, this would require Nevadans to retrain in new jobs or careers.
Education
[edit]Education in Nevada is achieved through public and private elementary, middle, and high schools, as well as colleges and universities.
A May 2015 educational reform law expanded school choice options to 450,000 Nevada students who are at up to 185% of the federal poverty level. Education savings accounts (ESAs) are enabled by the new law to help pay the tuition for private schools. Alternatively, families "can use funds in these accounts to also pay for textbooks and tutoring".[128][129]
Approximately 86.9% of Nevada residents have attained at least a high school degree or equivalent, which is below the national average of 88.6%.[130]
Public school districts
[edit]Public school districts in Nevada include:
- Carson City School District
- Churchill County School District
- Clark County School District, the fifth largest school district in the United States
- Douglas County School District
- Elko County School District
- Esmeralda County School District
- Eureka County School District
- Humboldt County School District
- Lander County School District
- Lincoln County School District
- Lyon County School District
- Mineral County School District
- Nye County School District
- Pershing County School District
- Storey County School District
- Washoe County School District
- White Pine County School District
Colleges and universities
[edit]Research institutes
[edit]The Nevada Aerospace Hall of Fame provides educational resources and promotes the aerospace and aviation history of the state.[131]
Law and government
[edit]Government
[edit]
Under the Constitution of the State of Nevada, the powers of the Nevada government are divided among three separate departments: the executive consisting of the governor of Nevada and their cabinet along with the other elected constitutional officers; the legislative consisting of the Nevada Legislature, which includes the Assembly and the Senate; and the judicial consisting of the Supreme Court of Nevada and lower courts.
The governor is the chief magistrate of Nevada,[132] the head of the executive department of the state's government,[132] and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces.[133] The current governor is Joe Lombardo, a Republican. The executive branch also consists of an independently elected lieutenant governor, secretary of state, state treasurer, state controller, and attorney general who function as a check and balance on the power of the governor.[134]
The Nevada Legislature is a bicameral body divided into an Assembly and Senate. Members of the Assembly serve two years, and members of the Senate serve four years. Both houses of the Nevada Legislature enacted term limits starting in 2010, with senators and assemblymen/women who are limited to a maximum of twelve years in each body (by appointment or election which is a lifetime limit) – a provision of the constitution which was upheld by the Supreme Court of Nevada in a unanimous decision. Each session of the legislature meets for a constitutionally mandated 120 days in every odd-numbered year, or longer if the governor calls a special session.
On December 18, 2018, Nevada became the first in the United States with a female majority in its legislature. Women hold nine of the 21 seats in the Nevada Senate, and 23 of the 42 seats in the Nevada Assembly.[135]
The Supreme Court of Nevada is the state supreme court and the head of the Nevada Judiciary. Original jurisdiction is divided between the district courts (with general jurisdiction), and justice courts and municipal courts (both of limited jurisdiction). Appeals from District Courts are made directly to the Nevada Supreme Court, which under a deflective model of jurisdiction, has the discretion to send cases to the Court of Appeals for final resolution.[136]
Incorporated towns in Nevada, known as cities, are given the authority to legislate anything not prohibited by law. A recent movement has begun to permit home rule to incorporate Nevada cities to give them more flexibility and fewer restrictions from the Legislature. Town Boards for unincorporated towns are limited local governments created by either the local county commission, or by referendum, and form a purely advisory role and in no way diminish the responsibilities of the county commission that creates them.
State agencies
[edit]- Attorney General
- Department of Business & Industry
- Department of Conservation & Natural Resources
- Consumer Health Assistance
- Controller's Office
- Department of Corrections
- Nevada Department of Cultural Affairs
- Nevada Commission on Economic Development
- Department of Education
- Nevada Secretary of State, Election Division
- Department of Employment, Training & Rehabilitation
- Gaming Control Board
- Governor's Office
- Nevada Film Office
- Department of Health and Human Services
- Department of Information Technology
- Department of Justice
- Lieutenant Governor
- Nevada Military Department
- Division of Minerals, Commission on Mineral Resources
- Department of Motor Vehicles
- Department of Personnel
- Advisory Council for Prosecuting Attorneys
- Public Employees Benefit Program
- Public Employees Retirement System
- Department of Public Safety
- Nevada Public Utilities Commission
- Department of Secretary of State
- Department of Taxation
- Commission on Tourism
- Department of Transportation
- Nevada State Treasurer
- Universities and Community Colleges of Nevada
- Nevada Office of Veterans' Services
- Western Interstate Commission for Higher Education
- Nevada Department of Wildlife
- Board of Museums and History
Law
[edit]
In 1900, Nevada's population was the smallest of all states and was shrinking, as the difficulties of living in a "barren desert" began to outweigh the lure of silver for many early settlers. Historian Lawrence Friedman has explained what happened next:
Nevada, in a burst of ingenuity, built an economy by exploiting its sovereignty. Its strategy was to legalize all sorts of things that were illegal in California ... after the easy divorce came easy marriage and casino gaming. Even prostitution is legal in Nevada, in any county that decides to allow it. Quite a few of them do.[137]
With the advent of air conditioning for summertime use and Southern Nevada's mild winters, the fortunes of the state began to turn around, as it did for Arizona, making these two states the fastest growing in the Union.
Prostitution
[edit]Nevada is the only state where prostitution is legal – in a licensed brothel in a county which has specifically voted to permit it. It is illegal in larger jurisdictions such as Clark County (which contains Las Vegas), Washoe County (which contains Reno), and the independent city of Carson City.
Divorce
[edit]Nevada's early reputation as a "divorce haven" arose from the fact that before the no-fault divorce revolution in the 1970s, divorces were difficult to obtain in the United States. Already having legalized gambling and prostitution, Nevada continued the trend of boosting its profile by adopting one of the most liberal divorce statutes in the nation. This resulted in Williams v. North Carolina (1942), 317 U.S. 287 (1942), in which the U.S. Supreme Court ruled North Carolina had to give "full faith and credit" to a Nevada divorce. The Court modified its decision in Williams v. North Carolina (1945), 325 U.S. 226 (1945), by holding a state need not recognize a Nevada divorce unless one of the parties was domiciled there at the time the divorce was granted and the forum state was entitled to make its own determination.
As of 2009, Nevada's divorce rate was above the national average.[138]
Taxes
[edit]Nevada's tax laws are intended to draw new residents and businesses to the state. Nevada has no personal income tax or corporate income tax.[139] Since Nevada does not collect income data it cannot share such information with the federal government, the IRS.[140]
The state sales tax (similar to VAT or GST) in Nevada is variable depending upon the county. The statewide tax rate is 6.85%, with five counties (Elko, Esmeralda, Eureka, Humboldt, and Mineral) charging this amount. Counties may impose additional rates via voter approval or through approval of the state legislature; therefore, the applicable sales tax varies by county from 6.85% to 8.375% (Clark County). Clark County, which includes Las Vegas, imposes four separate county option taxes in addition to the statewide rate: 0.25% for flood control, 0.50% for mass transit, 0.25% for infrastructure, and 0.25% for more law enforcement. In Washoe County, which includes Reno, the sales tax rate is 7.725%, due to county option rates for flood control, the ReTRAC train trench project, and mass transit, and an additional county rate approved under the Local Government Tax Act of 1991.[141] The minimum Nevada sales tax rate changed on July 1, 2009.[142]
The lodging tax rate in unincorporated Clark County, which includes the Las Vegas Strip, is 12%. Within the boundaries of the cities of Las Vegas and Henderson, the lodging tax rate is 13%.
Corporations such as Apple Inc. allegedly have set up investment companies and funds in Nevada to avoid paying taxes.[143]
LGBT rights
[edit]In 2009, the Nevada Legislature passed a bill creating a domestic partnership registry which enables same-sex couples to enjoy the same rights as married couples. Due to the landmark decision in the case of Obergefell v. Hodges, 576 U.S. 644 (2015), same-sex marriage was outright legalized in the state.
Incorporation
[edit]Nevada provides a friendly environment for the formation of corporations, and many (especially California) businesses have incorporated in Nevada to take advantage of the benefits of the Nevada statute. Nevada corporations offer great flexibility to the board of directors and simplify or avoid many of the rules that are cumbersome to business managers in some other states. In addition, Nevada has no franchise tax, although it does require businesses to have a license for which the business has to pay the state.
Financial institutions
[edit]Similarly, many U.S. states have usury laws limiting the amount of interest a lender can charge, but federal law allows corporations to "import" these laws from their home state. Nevada has no cap on interest rates that may be agreed to in contracts.[144]
Alcohol and other drugs
[edit]Nevada has very liberal alcohol laws. Bars are permitted to remain open 24 hours, with no "last call". Liquor stores, convenience stores and supermarkets may also sell alcohol 24 hours per day and may sell beer, wine and spirits.
In 2016, Nevada voters approved Question 2, which legalized the possession, transportation and cultivation of personal use amounts of marijuana for adults age 21 years and older, and authorized the creation of a regulated market for the sale of marijuana to adults age 21 years and older through state-licensed retail outlets.[145] Nevada voters had previously approved medical marijuana in 2000, but rejected marijuana legalization in a similar referendum in 2006. Marijuana in all forms remains illegal under federal law.
Aside from cannabis legalization, non-alcohol drug laws are a notable exception to Nevada's otherwise libertarian principles. It is notable for having the harshest penalties for drug offenders in the country. Nevada remains the only state to still use mandatory minimum sentencing guidelines for possession of drugs.[146]
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) reported, in their Behavioral Health Barometer for Nevada, published in 2014, changes to substance abuse patterns and addiction across the southwestern state.[147] Between 2012 and 2013, adolescents in Nevada abused illicit substances at a slightly higher percentage than nationally. 10.2 percent of Nevada's adolescents abused illicit drugs compared to 9.2 percent across the United States. Between 2009 and 2013, 11.7 percent of all adolescents in the state reported abusing illicit, intoxicating substances in the month prior to the survey; this represents 25,000 adolescents.
Smoking
[edit]Nevada voters enacted a smoking ban ("The Nevada Clean Indoor Air Act") in November 2006 which became effective on December 8, 2006. It outlaws smoking in most workplaces and public places. Smoking is permitted in bars, but only if the bar serves no food, or the bar is inside a larger casino. Smoking is also permitted in casinos, certain hotel rooms, tobacco shops, and brothels.[148] However, some businesses do not obey this law and the government tends not to enforce it.[149] In 2011, smoking restrictions in Nevada were relaxed for certain places which allow only people 21 or older inside.[150]
Crime
[edit]In 2006, the crime rate in Nevada was about 24% higher than the national average rate, though crime has since decreased. Property crimes accounted for about 85% of the total crime rate in Nevada, which was 21% higher than the national rate. The remaining 20.3% were violent crimes.[151] A complete listing of crime data in the state for 2013 can be found here:[152]
Politics
[edit]| Party | Total voters | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | 615,541 | 29.25% | |
| Republican | 615,539 | 29.25% | |
| Independent American | 94,460 | 4.49% | |
| Libertarian | 16,129 | 0.77% | |
| Other parties | 37,942 | 1.80% | |
| Nonpartisan | 725,071 | 34.45% | |
| Total | 2,104,682 | 100.00% | |
State politics
[edit]
Due to heavy growth in the southern portion of the state, there is a noticeable divide between the politics of northern and southern Nevada. Historically, northern Nevada has been very Republican. The more rural counties of the north are among the most conservative regions of the state. Carson City, the state's capital, is a Republican-leaning swing city/county. Washoe County, home to Reno, has historically been strongly Republican, but now has become a fairly balanced swing county, like the state as a whole. Clark County, home to Las Vegas, has been a stronghold for the Democratic Party since it was founded in 1909, having voted Republican only six times and once for a third-party candidate, although in recent times becoming more competitive, most notably in the 2024 Presidential Election where the Democratic Party's margin of victory was only 2.63 percentage points to Republicans.[154] Clark and Washoe counties have long dominated the state's politics. Between them, they cast 87% of Nevada's vote, and elect a substantial majority of the state legislature. The last Republican to carry Clark County was George H. W. Bush in 1988, and the last Republican to carry Washoe County was George W. Bush in 2004. The great majority of the state's elected officials are from either Las Vegas or Reno.[155] Donald Trump was able to carry Nevada with a statewide majority in 2024, despite losing both Clark and Washoe.
In 2014, Republican Adam Laxalt, despite losing both Clark and Washoe counties, was elected Attorney General. However, he had lost Clark County only by 5.6% and Washoe County by 1.4%, attributable to lower turnout in these counties.[156]
National politics
[edit]
Nevada has been won by the winner of nearly every presidential election since its first in 1864, only being carried by the defeated candidate eight times since statehood, most of which were before 1900. Since 1912 Nevada has been carried by the presidential victor the most out of any state (27 of 29 elections), the only exceptions being 1976 when it voted for Gerald Ford over Jimmy Carter and 2016 when the state was carried by Hillary Clinton over Donald Trump. This gives the state status as a political bellwether. It was one of only three states won by John F. Kennedy in the American West in the election of 1960, albeit narrowly.[157] The state's U.S. Senators are Democrats Catherine Cortez Masto and Jacky Rosen. The Governorship is held by Joe Lombardo, a Republican.
Elections
[edit]Nevada is the only U.S. state to have a none of the above option available on its ballots. Officially called None of These Candidates, the option was first added to the ballot in 1975 and is used in all statewide elections, including president, US Senate and all state constitutional positions. In the event "None of These Candidates" receives a plurality of votes in the election, the candidate with the next-highest total is elected.[158]
In a 2020 study, Nevada was ranked as the 23rd on the "Cost of Voting Index", which is a measure of "the ease of voting across the United States."[159]
Culture
[edit]Entertainment and tourism
[edit]Resort areas like Las Vegas, Reno, Lake Tahoe, and Laughlin attract visitors from around the nation and world. In fiscal year 2022 Nevada casinos (not counting those with annual revenue under a million dollars) brought in US$10.7 billion in gaming revenue and another US$15.7 billion in non-gaming revenue.[160]
Nevada has by far the most hotel rooms per capita in the United States. According to the American Hotel and Lodging Association, there were 187,301 rooms in 584 hotels (of 15 or more rooms). The state is ranked just below California, Texas, Florida, and New York in the total number of rooms, but those states have much larger populations. Nevada has one hotel room for every 14 residents, far above the national average of one hotel room per 67 residents.[161]
Prostitution is legal in parts of Nevada in licensed brothels, but only counties with populations under 400,000 have the option to legalize it. Although prostitution is not a major part of the Nevada economy, employing roughly 300 women as independent contractors, it is a very visible endeavor. Of the 14 counties permitted to legalize prostitution under state law, eight have chosen to legalize brothels. State law prohibits prostitution in Clark County (which contains Las Vegas), and Washoe County (which contains Reno). However, prostitution is legal in Storey County, which is part of the Reno–Sparks metropolitan area.
Sports
[edit]The Las Vegas Valley is home to the Vegas Golden Knights of the National Hockey League who began to play in the 2017–18 NHL season at T-Mobile Arena on the Las Vegas Strip in Paradise, the Las Vegas Raiders of the National Football League who began play at Allegiant Stadium in Paradise in 2020 after moving from Oakland, California, and the Las Vegas Aces of the WNBA who began playing in 2018 at Mandalay Bay Events Center after relocating from San Antonio. The Oakland Athletics of Major League Baseball plan to move to Las Vegas by 2027.[162][163]
Nevada takes pride in college sports, most notably its college football. College teams in the state include the Nevada Wolf Pack (representing the University of Nevada, Reno) and the UNLV Rebels (representing the University of Nevada, Las Vegas), both in the Mountain West Conference (MW).
UNLV is most remembered for its men's basketball program, which experienced its height of supremacy in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Coached by Jerry Tarkanian, the Runnin' Rebels became one of the most elite programs in the country. In 1990, UNLV won the Men's Division I Championship by defeating Duke 103–73, which set tournament records for most points scored by a team and largest margin of victory in the national title game.
In 1991, UNLV finished the regular season undefeated, a feat that would not be matched in Division I men's basketball for more than 20 years. Forward Larry Johnson won several awards, including the Naismith Award. UNLV reached the Final Four yet again, but lost their national semifinal against Duke 79–77. The Runnin' Rebels were the Associated Press pre-season No. 1 back to back (1989–90, 1990–91). North Carolina is the only other team to accomplish that (2007–08, 2008–09).
The state's involvement in major-college sports is not limited to its local schools. In the 21st century, the Las Vegas area has become a significant regional center for college basketball conference tournaments. The MW, West Coast Conference, and Western Athletic Conference all hold their men's and women's tournaments in the area, and the Pac-12 holds its men's tournament there as well. The Big Sky Conference, after decades of holding its men's and women's conference tournaments at campus sites, began holding both tournaments in Reno in 2016.
Las Vegas has hosted several professional boxing matches, most recently at the MGM Grand Garden Arena with bouts such as Mike Tyson vs. Evander Holyfield, Evander Holyfield vs. Mike Tyson II, Oscar De La Hoya vs. Floyd Mayweather Jr. and Oscar De La Hoya vs. Manny Pacquiao and at the newer T-Mobile Arena with Canelo Álvarez vs. Amir Khan.
Along with significant rises in popularity in mixed martial arts (MMA), a number of fight leagues such as the UFC have taken interest in Las Vegas as a primary event location due to the number of suitable host venues. The Mandalay Bay Events Center and MGM Grand Garden Arena are among some of the more popular venues for fighting events such as MMA and have hosted several UFC and other MMA title fights. The city has held the most UFC events with 86 events.
The state is also home to the Las Vegas Motor Speedway, which hosts NASCAR's Pennzoil 400 and South Point 400. Two venues in the immediate Las Vegas area host major annual events in rodeo. The Thomas & Mack Center, built for UNLV men's basketball, hosts the National Finals Rodeo. The PBR World Finals, operated by the bull riding-only Professional Bull Riders, was also held at the Thomas & Mack Center before moving to T-Mobile Arena in 2016.
The state is also home to famous tennis player, Andre Agassi, and current baseball superstar Bryce Harper.
List of teams
[edit]Major professional teams
[edit]| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Raiders | Football | NFL | Allegiant Stadium (65,000) | 2020 | 3[f] |
| Vegas Golden Knights | Ice hockey | NHL | T-Mobile Arena (17,500) | 2017 | 1 |
| Las Vegas Aces | Women's basketball | WNBA | Michelob Ultra Arena (12,000) | 2018 | 2 |
Minor professional teams
[edit]| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Aviators | Baseball | MiLB (AAA–PCL) | Las Vegas Ballpark (10,000) | 1983 | 2 |
| Reno Aces | Greater Nevada Field (9,013) | 2009 | 2 | ||
| Vegas Royals | Basketball | ABA | 0 | ||
| Henderson Silver Knights | Ice hockey | AHL | Dollar Loan Center (5,567) | 2020 | 0 |
| Tahoe Knight Monsters | ECHL | Tahoe Blue Event Center (5,000) | 2024 | 0 | |
| Las Vegas Lights FC | Soccer | USLC | Cashman Field (9,334) | 2018 | 0 |
| Nevada Storm | Women's football | WFA | Damonte Ranch High School (N/A) Fernley High School (N/A) Galena High School (N/A) |
2008 | 0 |
| Sin City Trojans | Desert Pines High School (N/A) | 0 | |||
| Vegas Knight Hawks | Indoor football | IFL | Dollar Loan Center (6,019) | 2021 | 0 |
| Las Vegas Desert Dogs | Box lacrosse | NLL | Michelob Ultra Arena (12,000) | 0 |
Amateur teams
[edit]| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reno Ice Raiders | Ice hockey | MWHL | Reno Ice | 2015 | 0 |
| Vegas Jesters | City National Arena (600) | 2012 | 0 | ||
| Las Vegas Thunderbirds | USPHL | 2019 | 0 | ||
| Las Vegas Legends | Soccer | NPSL | Peter Johann Memorial Field (2,500) | 2021 | 0 |
| Nevada Coyotes FC | UPSL | Rio Vista Sports Complex (N/A) | 2016 | 0 |
College teams
[edit]| School | Team | League | Division | Conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV) | UNLV Rebels | NCAA | NCAA Division I | Mountain West |
| University of Nevada, Reno (UNR) | Nevada Wolf Pack | |||
| College of Southern Nevada (CSN) | CSN Coyotes | NJCAA | NJCAA Division I | Scenic West |
| Western Nevada College (WNC) | WNC Wildcats |
Military
[edit]
Several United States Navy ships have been named USS Nevada in honor of the state. They include:
Area 51 is near Groom Lake, a dry salt lake bed. The much smaller Creech Air Force Base is in Indian Springs, Nevada; Hawthorne Army Depot in Hawthorne; the Tonopah Test Range near Tonopah; and Nellis AFB in the northeast part of the Las Vegas Valley. Naval Air Station Fallon in Fallon; NSAWC, (pronounced "EN-SOCK") in western Nevada. NSAWC consolidated three Command Centers into a single Command Structure under a flag officer on July 11, 1996. The Naval Strike Warfare Center based at NAS Fallon since 1984, was joined with the Navy Fighter Weapons School (TOPGUN) and the Carrier Airborne Early Warning Weapons School, which both moved from NAS Miramar as a result of a Base Realignment and Closure decision in 1993 which transferred that installation back to the Marine Corps as MCAS Miramar. The Seahawk Weapon School was added in 1998 to provide tactical training for Navy helicopters.
These bases host a number of activities including the Joint Unmanned Aerial Systems Center of Excellence, the Naval Strike and Air Warfare Center, Nevada Test and Training Range, Red Flag, the U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds, the United States Air Force Warfare Center, the United States Air Force Weapons School, and the United States Navy Fighter Weapons School.
See also
[edit]- Index of Nevada-related articles
- Outline of Nevada – organized list of topics about Nevada
- List of people from Nevada
Notes
[edit]- ^ a b Elevation to North American Vertical Datum of 1988
- ^ The distinction of highest point in Nevada goes to the summit of Boundary Peak, so named because it is very near the Nevada–California border, at the northern terminus of the White Mountains. However, Boundary Peak can be considered a subsidiary summit of Montgomery Peak, whose summit is in California, since the topographic prominence of Boundary Peak is only 253 feet (77 m), which falls under the often used 300-foot (91 m) cutoff for an independent peak. Also, Boundary Peak is less than 1 mile (1.6 km) away from its higher neighbor. Hence Boundary Peak can be described as not being wholly within Nevada. By contrast, the prominence of Wheeler Peak, 13,063 feet (3,982 m), is quite large and in fact it is the twelfth largest in the contiguous United States. Wheeler Peak is the highest point in a radius of more than 200 square miles (520 km2) and is entirely within the state of Nevada.
- ^ Also sometimes placed in the Mountain West and Southwestern United States
- ^ The National Archives press release states that the cost was $4,313.27, but the amount $4,303.27 is actually written on the document.
- ^ Persons of Hispanic or Latino origin are not distinguished between total and partial ancestry.
- ^ Two titles were won when the team was based in Oakland, California and one was won when they were based in Los Angeles, California.
References
[edit]- ^ "Boundary". NGS Data Sheet. National Geodetic Survey, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, United States Department of Commerce. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ a b "Elevations and Distances in the United States". United States Geological Survey. 2009. Archived from the original on October 15, 2011. Retrieved October 24, 2011.
- ^ "United States Census Quick Facts Nevada". Retrieved January 9, 2025.
- ^ "Household Income in States and Metropolitan Areas: 2023" (PDF). Retrieved January 12, 2025.
- ^ "Nevada". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- ^ "Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas Population Totals: 2010-2017". 2017 Population Estimates. United States Census Bureau, Population Division. Archived from the original on September 26, 2018. Retrieved March 2, 2019.
- ^ "City and Town Population Totals: 2010-2017". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on March 28, 2019. Retrieved March 2, 2019.
- ^ "The Almanac of American Politics on Nevada and Lombardo". July 13, 2023.
- ^ Rines, George Edwin, ed. (1920). . Encyclopedia Americana.
- ^ Federal Land Ownership: Overview and Data (Report). Congressional Research Service. February 21, 2020. Retrieved September 8, 2024.
- ^ Rocha, Guy "Myth No. 12 – Why Did Nevada Become a State?" Archived October 24, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Nevada State Library and Archives, accessed January 9, 2011
- ^ "Race and Hispanic Origin: 1790 to 1990 by State" (PDF). US Census. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 21, 2014. Retrieved July 16, 2014.
- ^ Bill Bible (August 11, 2000). "Protect gaming's legacy". Las Vegas Sun. Where I Stand (opinion). Archived from the original on July 12, 2017. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ Jain, Priya (July 21, 2010). "Betty Goes Reno". Slate. ISSN 1091-2339. Archived from the original on December 29, 2017. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ "Nevada Employment & Unemployment Estimates for November 2010" Archived May 25, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Nevada Department of Employment, Training, and Rehabilitation.
- ^ "Mining FAQs". Nevada Mining Association. February 23, 2018. Archived from the original on January 23, 2018. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ Bornstein, Seth (February 15, 2022). "West megadrought worsens to driest in at least 1,200 years". Las Vegas Sun. Associated Press. Archived from the original on March 6, 2022. Retrieved September 12, 2022.
- ^ "Nevada". WordReference.com. Archived from the original on December 25, 2007. Retrieved February 24, 2007.
- ^ "Nevada". Online Etymology Dictionary. Archived from the original on September 1, 2021. Retrieved September 1, 2021.
- ^ McCabe, Francis (October 18, 2018). "You Say Nevada, I Say Nevada…". University of Nevada, Las Vegas. Archived from the original on August 1, 2019. Retrieved November 26, 2019.
- ^ Ladefoged, Peter; Johnson, Keith (2010), A Course in Phonetics (6th ed.), Boston, Massachusetts: Wadsworth Publishing, p. 227, ISBN 978-1-4282-3126-9
- ^ Wells, John C. (1982). Accents of English. Vol. 3: Beyond the British Isles (pp. i–xx, 467–674). Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511611766. ISBN 0-52128541-0.. Page 476.
- ^ Clifton, Guy (August 22, 2010). "You heard it right: Bill would let them say Ne-VAH-da". Reno Gazette-Journal.
- ^ "Nevada: A World Within. A State Apart. | Nevada Travel & Tourism". Travel Nevada. Archived from the original on December 29, 2013. Retrieved October 7, 2016.
- ^ "Nevada Tourism License Plate". Nevada Department of Motor Vehicles. Archived from the original on July 3, 2019. Retrieved July 3, 2019.
- ^ "History of Nevada". Archived from the original on November 6, 2021. Retrieved March 14, 2022.
- ^ Sapp, Rick (October 16, 2018). Native Americans State by State. Book Sales. ISBN 9780785835875. Archived from the original on April 17, 2022. Retrieved March 25, 2022.
- ^ "Explorers and Settlers in Nevada" (PDF). Washoe County School District. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ "Online Etymology Dictionary". Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ Zorn, Roman J.; McNamee, Gregory Lewis; et al. (2023). "Nevada". Britannica. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ "The U.S. Congress admits Nevada as the 36th state". The History Channel. October 29, 2020. Retrieved September 30, 2023.
- ^ "National Archives Celebrates the 145th Anniversary of Nevada Statehood". National Archives of the United States. September 23, 2009. Archived from the original on October 20, 2011. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
- ^ Rocha Guy, Historical Myth a Month: Why Did Nevada Become A State? Archived January 13, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Tannenbaum, Austin (March 10, 2023). "Did Nevada's original southern boundary exclude Las Vegas?". The Nevada Independent. Retrieved December 1, 2024.
- ^ Coffin, Laura A. (9 March 2012). The Bottle Houses of the Old West (archive). New Bedford Museum of Glass. Retrieved 13 February 2024. "In 1906, at the age of 76...[Tom Kelly] laid all the bottles on their sides, with the bottoms facing out, and mortared them together with adobe mud."
- ^ Moe, Al W. Nevada's Golden Age of Gambling, Puget Sound Books Archived March 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, 2002, p. 18
- ^ a b National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, N.C., and Storm Phillips, Stormfax, Inc.
- ^ "Nevada Mountains". PeakVisor. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ Osborn, Liz. "Driest states". Currentresults.com. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "Nevada climate averages". Weatherbase. Archived from the original on October 9, 2015. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ Federal Writers' Project (1940). Nevada: a guide to the Silver state. US History Publishers. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-60354-027-8.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - ^ a b "Political History of Nevada". Nevada State Library and Archives. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved August 17, 2007.
- ^ "Visitors". Clarkcountynv.gov. Archived from the original on July 17, 2014. Retrieved July 27, 2014.
- ^ Laws of the Territory of Nevada passed at the first regular session of the Legislative Assembly. San Francisco, CA: Valentine & Co. 1862. pp. 289–291. Archived from the original on July 7, 2014. Retrieved May 14, 2014.
- ^ "Nevada's Census Population By County 2020 and 2022". Archived from the original on April 22, 2022. Retrieved July 2, 2023.
- ^ "2020 Nevada QuickFacts". U.S. Census Bureau. August 18, 2021. Archived from the original on April 22, 2022. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ "Wilderness.net". Wilderness.net. Archived from the original on July 22, 2010. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- ^ O'Daly, Lisa. "Van Sickle Bi-State Park – Sierra Nevada Geotourism MapGuide". Sierranevadageotourism.org. Archived from the original on September 26, 2018. Retrieved September 25, 2018.
- ^ "Historical Population Change Data (1910–2020)". Census.gov. United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on April 29, 2021. Retrieved May 1, 2021.
- ^ "QuickFacts Nevada; United States". 2022 Population Estimates. United States Census Bureau, Population Division. July 1, 2022. Archived from the original on April 6, 2022. Retrieved January 2, 2023.
- ^ "Cumulative Estimates of the Components of Resident Population Change for the United States, Regions, States, and Puerto Rico: April 1, 2020 to July 1, 2021" (xlsx). U.S. Census Bureau. December 21, 2021. Archived from the original on March 24, 2022. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ "Download the Centers of Population by State: 2020" (txt). U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on April 1, 2022. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ "Pahrump CDP QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau". Quickfacts.census.gov. Archived from the original on May 9, 2022. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ Aisch, Gregor; Gebeloff, Robert; Quealy, Kevin (August 14, 2014). "Where We Came from and Where We Went, State by State". The New York Times. Archived from the original on March 31, 2019. Retrieved March 16, 2019.
- ^ "2007-2022 PIT Counts by State".
- ^ "The 2022 Annual Homelessness Assessment Report (AHAR) to Congress" (PDF).
- ^ "P004HISPANIC OR LATINO, AND NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO BY RACE [73] - Nevada". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ "P2 HISPANIC OR LATINO, AND NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO BY RACE - 2010: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) - Nevada". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ "P2 HISPANIC OR LATINO, AND NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO BY RACE - 2020: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) - Nevada". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ "Race and Ethnicity in the United States: 2010 Census and 2020 Census". census.gov. United States Census Bureau. August 12, 2021. Archived from the original on August 15, 2021. Retrieved September 26, 2021.
- ^ "Grid View: Table B03001 - Census Reporter". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ "Grid View: Table B04006 - Census Reporter". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ "Grid View: Table B02018 - Census Reporter". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ a b c "Historical Census Statistics on Population Totals By Race, 1790 to 1990, and By Hispanic Origin, 1970 to 1990, For The United States, Regions, Divisions, and States". Census.gov. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008. Retrieved July 27, 2014.
"Table 43. Nevada Race and Hispanic Origin: 1860 to 1990 Archived May 14, 2015, at the Wayback Machine". (PDF) - ^ "Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2000 Archived July 24, 2017, at the Wayback Machine" (PDF). United States Census Bureau
- ^ "2010 Census Data". Census.gov. Archived from the original on May 22, 2017. Retrieved July 27, 2014.
- ^ "Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2020 Demographic Profile Data (DP-1): Nevada". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 16, 2024.
- ^ Exner, Rich (June 3, 2012). "Americans under age 1 now mostly minorities, but not in Ohio: Statistical Snapshot". cleveland.com. Advance Digital. Archived from the original on July 15, 2016. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: Nevada". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on November 30, 2018. Retrieved November 29, 2018.
- ^ "Grid View: Table B02018 - Census Reporter". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ Stefoff, Rebecca (2010). Nevada. Marshall Cavendish. ISBN 9780761447283. Archived from the original on February 20, 2021. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Shepperson, Wilbur (1970). "The Immigrant in Nevada's Short Stories and Biographical Essays" (PDF). Nevada Historical Society Quarterly. 13 (3): 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 26, 2021. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ^ "Immigration and Ethnic Diversity in Nevada* Introduction".
- ^ "A HISTORICAL OVERVIEW OF IMMIGRATION IN NEVADA".
- ^ "History of Nevada Indians **". Archived from the original on February 17, 2020. Retrieved February 17, 2020.
- ^ "Census data shows communities of color are the new Nevada". August 16, 2021.
- ^ Davidson, Michael Scott (August 12, 2021). "Census: Nevada ranks high in diversity, Hispanics fuel growth". Las Vegas Review-Journal.
- ^ Tuman, John; Damore, David; Agreda, Maria (June 1, 2013). "Immigration and the Contours of Nevada's Latino Population". Brookings Mountain West Publications: 1–18.
- ^ "First cut on census data: Nevada is diversifying, but it's complicated". Guinn Center For Policy Priorities. August 25, 2021.
- ^ "Immigrants in Nevada". June 2015. Archived from the original on February 24, 2020. Retrieved March 15, 2020.
- ^ "Desert, Wildlife, Flora". Encyclopedia Britannica. July 26, 1999.
- ^ "Nevada". info-america-usa.com.
- ^ Schnell, Mychael (August 12, 2021). "Hawaii is most diverse state in the US, census shows". The Hill.
- ^ "Census: Nevada becomes more populous and diverse, but growth slows". August 12, 2021.
- ^ "data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 25, 2018. Retrieved September 25, 2018.
- ^ "data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 26, 2018. Retrieved September 25, 2018.
- ^ "data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 26, 2018. Retrieved September 25, 2018.
- ^ "data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 3, 2018. Retrieved May 5, 2018.
- ^ "Births: Final Data for 2017" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on February 1, 2019. Retrieved February 21, 2019.
- ^ "Data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2019. Retrieved December 21, 2019.
- ^ "Data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 23, 2021. Retrieved March 30, 2021.
- ^ "Data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 10, 2022. Retrieved February 20, 2022.
- ^ "Data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Retrieved February 3, 2022.
- ^ "Data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Retrieved April 5, 2024.
- ^ "Data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Retrieved April 12, 2025.
- ^ "$1.3 billion for 288 jobs: The failure of government-subsidized renewable energy". Nevadabusiness.com. October 1, 2012. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ Robison, Jennifer (May 3, 2014). "Before mining and gambling, ranching shaped Nevada's culture". Las Vegas Review-Journal. Archived from the original on November 7, 2014. Retrieved November 7, 2014.
- ^ "2022 American Values Atlas: Religious Tradition". Public Religion Research Institute. February 24, 2023. Retrieved March 30, 2023.
- ^ "Mississippians Go to Church the Most; Vermonters, Least". Gallup.com. February 17, 2010. Archived from the original on September 27, 2013. Retrieved July 27, 2014.
- ^ "PRRI – American Values Atlas". ava.prri.org. Retrieved September 17, 2022.
- ^ "Religious Landscape Study". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. Retrieved September 17, 2022.
- ^ "The Association of Religion Data Archives | State Membership Report". www.thearda.com. Archived from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved November 22, 2013.
- ^ "Nevada | Data USA".
- ^ Summers, Keyonna (October 15, 2021). "Preserve Nevada: Indigenous Languages, Cultural Landmarks Among State's 'Most Endangered'". UNLV News Center. University of Nevada, Las Vegas. Archived from the original on April 24, 2022.
- ^ AB 246 Ballots for All: Improving Language Access for Nevada Voters (March 28, 2023). Presented by Selena Torres, Assemblywoman (D, NV-3) as an exhibit during debate on Assembly Bill 248. Presentation archived from the original March 30, 2023. (Note: AB 246 passed was passed by the legislature but vetoed by Governor Joe Lombardo.)
- ^ "Nevada Indian Tribes and Languages". www.native-languages.org. Retrieved September 2, 2024.
- ^ "American Indian and Alaska Native Tribes in the United States and Puerto Rico: 2010".
- ^ Frank, Dave. "Western Region Gold Deposits (completed project)". Archived from the original on June 7, 2013. Retrieved August 17, 2013.
- ^ "Bureau of Economic Analysis". Bea.gov. Archived from the original on January 16, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "GDP by State". Greyhill Advisors. Archived from the original on January 13, 2013. Retrieved September 23, 2011.
- ^ "GDP and Personal Income". Regional Data. Bureau of Economic Analysis. Archived from the original on March 29, 2019. Retrieved April 25, 2019.
- ^ "Per Capita Personal Income by State, Annual". FRED. St. Louis, MO: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Archived from the original on July 13, 2021. Retrieved July 13, 2021.
- ^ ""The 34th worst state" Truth in Accounting" (PDF). statedatalab.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 10, 2014. Retrieved July 27, 2014.
- ^ "Nevada Economy at a Glance". U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. United States Department of Labor. Archived from the original on July 13, 2021. Retrieved July 13, 2021.
- ^ Harding, Adella (August 17, 2023). "Gold Production in Nevada slips in 2022". Elko Daily Free Press. Archived from the original on November 26, 2023. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ^ Sheaffer, Kristin N. (January 31, 2023). Mineral Commodity Summaries 2023 (PDF). Reston, Virginia: U.S. Geological Survey. pp. 80–81. ISBN 978-1-4113-4504-1. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ^ Robison, Jennifer (May 3, 2014). "Before mining and gambling, ranching shaped Nevada's culture". Las Vegas Review-Journal. Archived from the original on December 29, 2024.
- ^ a b National Agricultural Statistics Service (2022). Census of Agriculture State Profile: Nevada (PDF) (Report). Washington, D.C.: United States Department of Agriculture. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 4, 2024.
- ^ "Nevada's Largest Employers – Statewide Archived April 25, 2012, at the Wayback Machine." Nevada Workforce Informer. Nevada Department of Employment, Training and Rehabilitation.
- ^ Rogers, Carl (September 2005). Pictures of Highway Shields: Nevada!. Lulu.com. ISBN 9781411663183.
- ^ Hernandez, Dan (January 13, 2016). "Nevada solar industry collapses after state lets power company raise fees". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ "Congress works to revive long-delayed plan to store nuclear waste in Yucca Mountain". USA Today. June 3, 2018. Archived from the original on August 1, 2019. Retrieved November 14, 2019.
- ^ Holder, Sarah (March 13, 2018). "For Low-Income Renters, the Affordable Housing Gap Persists". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on January 31, 2022. Retrieved December 6, 2021.
- ^ "Can Nevadans afford Nevada? A look at the state's housing, rental markets". FOX5 Las Vegas. Archived from the original on December 6, 2021. Retrieved December 6, 2021.
- ^ "American Community Survey (ACS)". Census.gov. Archived from the original on December 5, 2021. Retrieved December 6, 2021.
- ^ "Affordable Housing - Nevada HAND | Affordable Housing | Las Vegas". Nevada HAND. Archived from the original on December 6, 2021. Retrieved December 6, 2021.
- ^ "School Choice: Full Education Competition Comes To Nevada". Investors Business Daily. June 1, 2015. Archived from the original on July 15, 2015. Retrieved June 2, 2015.
- ^ "Nevada – Education Savings Accounts". Edchoice. Archived from the original on July 7, 2015. Retrieved June 5, 2015.
- ^ "Nevada". U.S. Census Bureau – Nevada. U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 15, 2020. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ "Nevada Aerospace Hall of Fame". Nvahof.org. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ a b NV Const. art. V, § 1.
- ^ NV Const. art. V, § 5.
- ^ Stewart, Michael J. "The Structure of Government: Executive Branch" (PDF). Nevada Legislative Counsel Bureau. Retrieved September 12, 2023.
- ^ Price, Michelle L. (December 18, 2018). "Nevada becomes 1st US state with female-majority Legislature". Associated Press. Archived from the original on December 20, 2018. Retrieved December 20, 2018.
- ^ "Court of Appeals". Nevada Judiciary. Archived from the original on August 12, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- ^ Lawrence M. Friedman, American Law in the Twentieth Century (New Haven: Yale University Press, 2002), pp. 596–597.
- ^ "Nevada's divorce rate exceeds national average – News – ReviewJournal.com". Lvrj.com. August 25, 2011. Archived from the original on May 24, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "The Tax Foundation – Tax Research Areas > Nevada". Tax Foundation. Archived from the original on June 22, 2012. Retrieved September 15, 2010.
- ^ Nicholas Shaxson: Treasure Islands, Tax Havens and the Men Who Stole the World; The Bodley Head, London, 2011
- ^ "Sales Tax Map" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on January 29, 2013. Retrieved May 4, 2013.
- ^ "Taxation Publications". Tax.state.nv.us. Archived from the original on August 13, 2010. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- ^ "The Agony and Ecstasy – and 'Disgrace' – of Steve Jobs". The Nation. November 9, 2011. Archived from the original on January 23, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "Nevada Interest Rates Laws". Archived from the original on December 31, 2021. Retrieved December 31, 2021.
- ^ "Initiative to Regulate and Tax Marijuana". Nevada Secretary of State. April 23, 2014. Archived from the original on August 17, 2016. Retrieved May 23, 2016.
- ^ "Las Vegas, Nevada "Possession of a Controlled Substance (Drug)" Laws". www.shouselaw.com. Archived from the original on November 27, 2018. Retrieved November 26, 2018.
- ^ "Addiction and Mental Health in Nevada". Desert Hope. Archived from the original on January 11, 2021. Retrieved January 28, 2021.
- ^ "State smoking ban sparks zone-change request for Gardnerville parcel Nevada Appeal serving Carson City, Nevada". Nevadaappeal.com. October 6, 2007. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- ^ "Have Nevada bars given up the smoking habit?". Kvbc.com. Archived from the original on September 29, 2011. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- ^ "Black & LoBello smoking ban loosened Archives " Black & LoBello". Blacklobellolaw.com. June 17, 2011. Archived from the original on November 29, 2014. Retrieved July 27, 2014.
- ^ "Overview of Nevada's CorrectionalSystem". NICIC. January 4, 2009. Archived from the original on February 16, 2008. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ^ "2013 Crime In Nevada Annual Report" (PDF). NV Repository. 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 29, 2014. Retrieved November 21, 2014.
- ^ "Voter Registration Statistics". Retrieved April 2, 2025.
- ^ "Clark County 2024 General Election Results".
- ^ "Political History of Nevada" (PDF).
- ^ "2014 Attorney General General Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Archived from the original on July 9, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ "2012 vs 1960". Daily Kos. November 9, 2012. Archived from the original on March 9, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "Not a fan of any candidate? In Nevada, you can vote for 'None of These Candidates'". PBS NewsHour. October 18, 2016. Archived from the original on September 12, 2018. Retrieved September 12, 2018.
- ^ Pomante II, Michael J.; Li, Quan (December 15, 2020). "Cost of Voting in the American States: 2020". Election Law Journal: Rules, Politics, and Policy. 19 (4): 503–509. doi:10.1089/elj.2020.0666. ISSN 1533-1296. S2CID 225139517.
- ^ "Nevada Gaming Abstract 2022". Nevada Gaming Control Board. 2022. Retrieved January 17, 2024.
- ^ "State-by-State Fact Sheets on Lodging Industry". Archived from the original on May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Oakland A's close in on move to Las Vegas after signing land deal for stadium". The Guardian. April 20, 2023. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved April 20, 2023.
- ^ Dubow, Josh (April 20, 2023). "Oakland A's purchase land for new stadium in Las Vegas". SFGATE. Retrieved April 20, 2023.
External links
[edit]- "Nevada" (official state website).
- "Nevada State Guide". Library of Congress.
- "Nevada State Databases". ALA. Archived from the original on January 6, 2014. Retrieved May 11, 2008. Annotated list of searchable databases produced by Nevada state agencies and compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association.
- State Tourism website
- Nevada State Library and Archives
- Energy Profile for Nevada
- USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Nevada
- US Census Bureau
- 1875 County Map at Texas Tech Southwest Collection
- County Maps of Nevada Full color maps. List of cities, towns and county seats
- Nevada State Facts from USDA
- Forgotten Nevada – Ghost Towns and Mining Camps of Nevada
- Nevada's Historical Markers
- Nevada State Seal
 Geographic data related to Nevada at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Nevada at OpenStreetMap- Online Nevada Encyclopedia, Nevada Humanities
- Nevada Corporation Headquarters





