Lüneburg
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2015) |
Lüneburg
Lümborg (Low German) | |
|---|---|
 Panorama of Lüneburg from the water tower, with St. Johannis Church in the foreground to the right | |
Location of Lüneburg
within Lüneburg district  | |
 Location of Lüneburg | |
| Coordinates: 53°15′9″N 10°24′52″E / 53.25250°N 10.41444°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Lower Saxony |
| District | Lüneburg |
| Subdivisions | 14 districts |
| Government | |
| • Lord mayor (2021–26) | Claudia Kalisch[1] (Greens) |
| Area | |
• Total | 70.34 km2 (27.16 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 17 m (56 ft) |
| Population (2023-12-31)[2] | |
• Total | 77,511 |
| • Density | 1,102/km2 (2,854/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 21335–21337–21339 |
| Dialling codes | 04131 |
| Vehicle registration | LG |
| Website | www.hansestadt-lueneburg.de |
Lüneburg,[a] officially the Hanseatic City of Lüneburg[b] and also known in English as Lunenburg,[c] is a town in the German state of Lower Saxony. It is located about 50 km (31 mi) southeast of another Hanseatic city, Hamburg, and belongs to that city's wider metropolitan region. The capital of the district which bears its name, it is home to roughly 77,000 people.[3] Lüneburg's urban area, which includes the surrounding communities of Adendorf, Bardowick, Barendorf and Reppenstedt, has a population of around 103,000. Lüneburg has been allowed to use the title Hansestadt ('Hanseatic Town') in its name since 2007, in recognition of its membership in the former Hanseatic League. Lüneburg is also home to Leuphana University.
History
[edit]



Prehistory
[edit]The first signs of human presence in the area of Lüneburg date back to the time of Neanderthal Man: 56 axes, estimated at 150,000 years old, were uncovered during the construction in the 1990s of the autobahn between Ochtmissen and Bardowick.[4] The site of the discovery at Ochtmissen was probably a Neanderthal hunting location where huntsmen skinned and cut up the animals they had caught.
The area was almost certainly not continuously inhabited at that time, however, due to the various glaciations that lasted for millennia. The first indication of a permanent, settled farming culture in the area was found not far from the site of the Neanderthal discovery in the river Ilmenau between Lüne and Bardowick. This was an axe that is described as a Schuhleistenkeil or "shoe last wedge" due to its shape. It dates to the 6th century BC and is now in the collection of the Lüneburg Museum.
Since the Bronze Age, the Lüneburg hill known as the Zeltberg has concealed a whole range of prehistoric and early historic graves, which were laid out by people living in the area of the present-day town of Lüneburg. One of the oldest finds from this site is a so-called Unetice flanged axe (Aunjetitzer Randleistenbeil) which dates to 1900 BC.
The land within the town itself has also yielded a number of ice age urns that were already being reported in the 18th century. These discoveries are, however, like those from the Lüneburger Kalkberg — they went into the private collections of several 18th century scholars and, with a few exceptions, were lost when the scholars died.
Also worth mentioning in this regard are the Lombard Urnfield graves on the Lüneburg Zeltberg and Oedeme from the first few centuries AD. In the Middle Ages, there several discoveries were made on the site of the town, for example on the site of the old village of Modestorpe not far from St. John's Church (Johanniskirche), at the Lambertiplatz near the saltworks and in the old Waterside Quarter.
The ancient town may be that identified as Leufana or Leuphana (Greek: Λευφάνα), a town listed in Ptolemy (2.10) in the north of Germany on the west of the Elbe.
From village to commercial town
[edit]
Lüneburg was first mentioned in medieval records in a deed signed on 13 August, 956 AD, in which Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor granted "the tax from Lüneburg to the monastery built there in honour of Saint Michael" (German: den Zoll zu Lüneburg an das zu Ehren des heiligen Michaels errichtete Kloster, Latin: teloneum ad Luniburc ad monasterium sancti Michahelis sub honore constructum).[5] An older reference to the place in the Royal Frankish Annals for 795 states:ad fluvium Albim pervenit ad locum, qui dicitur Hliuni, i.e. "on the river Elbe, at the location, which is called Hliuni") and refers to one of the three core settlements of Lüneburg; probably the castle on the Kalkberg which was the seat of the Billunger nobles from 951. The Elbe-Germanic name Hliuni corresponds to the Lombard word for "refuge site".
From archaeological finds, it is clear that the area around Lüneburg had already been settled (in the museum of the Principality of Lüneburg, for example, there is a whole range of artefacts that were found here) and the saltworks had already started production.
According to tradition, the salt was first discovered by a hunter who observed a wild boar bathing in a pool of water, shot and killed it, and hung the coat up to dry. When it was dry, he discovered white crystals in the bristles — salt. Later he returned to the site of the kill and located the salt pool, the first production of salt on the site took place. In the town hall is a bone preserved in a glass case; legend has it that this is the preserved leg-bone of the boar. It was here that the Lüneburg Saltworks was subsequently established for many centuries.
In spite of its lucrative saltworks, Lüneburg was originally subordinated to the town of Bardowick only a few miles to the north. Bardowick was older and was an important trading post for the Slavs. Bardowick's prosperity – it had seven churches – was based purely on the fact that no other trading centres were tolerated. Only when Bardowick refused to pay allegiance to Henry the Lion it was destroyed by him in 1189, whereupon Lüneburg was given town privileges (Stadtrechte) and developed into the central trading post in the region in place of Bardowick.
The Polabian name for Lüneburg is Glain (written as Chlein or Glein in older German sources), probably derived from glaino (Slavonic: glina) which means "clay". In the Latin texts Lüneburg surfaces not only as the Latinised Lunaburgum, but also as Selenopolis.
Hanseatic period
[edit]


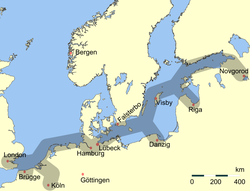
As a consequence of the monopoly that Lüneburg had for many years as a supplier of salt within the North German region, a monopoly not challenged until much later by French imports, it very quickly became a member of the Hanseatic League. The League was formed in 1158 in Lübeck, initially as a union of individual merchants, but in 1356 it met as a federation of trading towns at the first general meeting of the Hansetag. Lüneburg's salt was needed in order to pickle the herring caught in the Baltic Sea and the waters around Norway so that it could be preserved for food inland during periods of fasting when fish (not meat) was permitted.
The Scania Market at Scania in Sweden was a major fish market for herring and became one of the most important trade events in Northern Europe in the Middle Ages. Lüneburg's salt was in great demand and the town quickly became one of the wealthiest and most important towns in the Hanseatic League, together with Bergen and Visby (the fish suppliers) and Lübeck (the central trading post between the Baltic and the interior). In the Middle Ages salt was initially conveyed overland up the Old Salt Road to Lübeck. With the opening of the Stecknitz Canal in 1398 salt could be transported by cog from the Lübeck salt warehouses, the Salzspeicher.
Around the year 1235, the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg emerged, ruled by a family whose aristocratic lines repeatedly divided and re-united. The smaller states that kept re-appearing as a result, and which ranked as principalities, were usually named after the location of the ducal seat. Thus between 1267 and 1269 a Principality of Lüneburg was created for the first time, with Lüneburg as the seat of the royal Residenz. In 1371, in the wake of the Lüneburg War of Succession, rebel citizens threw the princes out of the town and destroyed their royal castle on the Kalkberg along with the nearby monastery. The state peace treaty in 1392 granted their demand to become a free imperial town, a status they were able to defend until 1637. The money now stayed in the town, enabling fine houses and churches to be built. In 1288, a Judenstrasse was recorded, indicating that there was a Medieval Jewish community in Lüneburg.[6]
In 1392, Lüneburg was accorded the staple right. This forced merchants who travelled through the area with their carts to stop in Lüneburg, unload their wares, and offer them for sale for a certain period. So that merchants could not go around Lüneburg, an impassable defensive barrier was built west of the town in 1397; a similar barrier was built east of the town in 1479.
The Lüneburg Prelates' War caused a crisis from 1446 to 1462. This was not a war in the proper sense, but rather a bitter dispute between the town council and those members of the clergy who were also part-owners of the town's saltworks. It was not resolved until the intervention of the Danish King Christian I, the Bishop of Schwerin and the Lübeck Bishop, Arnold Westphal.
In 1454, the citizens demanded even more influence over public life.
Since 2007, Lüneburg has once again held the title of a Hanseatic town.
Modern period to the end of the Second World War
[edit]The Old Salt Route connected the Hanseatic Lübeck and the Hanseatic town of Lüneburg.[8] With the demise of the Hanseatic League and the absence of herring around 1560, Falsterbo in Scania broke away as the biggest customers of Lüneburg's salt. Lüneburg rapidly became impoverished. Hardly any new houses were built in central Lüneburg after this time, which is why the historical appearance of the town centre has remained almost unchanged until the present day. The town became part of the Electorate of Hanover in 1708, the Kingdom of Westphalia in 1807, the First French Empire in 1810, the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814, and the Prussian Province of Hanover in 1866. In the centuries after the collapse of the Hanseatic League, it was as if Lüneburg had fallen into a slumber. Heinrich Heine, whose parents lived in Lüneburg from 1822 to 1826, called it his "residence of boredom" (Residenz der Langeweile). The horticulturist Curt Backeberg was born in Lüneburg in 1894. Near the end of the 19th century Lüneburg evolved into a garrison town, and it remained so until the 1990s.
After the Nazi anti-Jewish pogroms known as Kristallnacht in the night of November 9, 1938, the city ordered the Lüneburg Synagogue to be torn down at the costs of the local Jewish community.[9] In the Lüneburg Special Children's Ward, part of the Lüneburg State Mental Hospital, it is suspected that over 300 children were killed during the Second World War as part of the official Nazi child euthanasia programme.[10]
When World War II broke out, Lüneburg became a target. During the bombing of Lüneburg, the town was attacked 19 times between 1940 and 1945 but miraculously survived without major damage to its city center, unlike nearby Hamburg. The biggest and most destructive bombing on Lüneburg took place on 22 February. Between 10:10 and 14:15, 39 airplanes bombed the city and its surroundings. As a result, multiple trenches near the Lüneburg station and the station's air raid shelter were hit by bombs, killing a total 350 people. The railway bridge over the Dahlenburger Landstraße also collapsed. The houses around the railway station were severely damaged or completely destroyed. In Wandrahmstraße, the Lüneburg Museum, whose holdings had not been completely removed, was completely destroyed. Furthermore, the terminus of the Lüneburg-Bleckede railway line, the marshalling yard, a dairy on Lüner Weg and a factory in the Am Schwalbenberg street were severely damaged. A second big raid happened on 7 April 1945 with 13 aircraft. The target was once more the railway station and its surroundings, where a train with 400 prisoners from the Alter Banter Weg satellite camp near Wilhelmshaven, who were to be taken to Neuengamme, was parked. Because the prisoners were locked in the carriages, they were unable to flee when the bombs fell, killing 256 in total.[11] The goods station was completely destroyed, as were the waterworks and the Wachsbleiche factory. The teachers' seminar on Wilschenbrucher Weg, which housed an auxiliary hospital and was then used by the Leuphana University of Lüneburg, was badly damaged by a direct bomb hit, as was the auxiliary hospital Zur Hasenburg on Soltauer Straße. Many bombs also hit the Rote Feld, which was still largely undeveloped at the time. While the attacks resulted in 608 casualties, Lüneburg itself was largely spared and only a total of 270 homes were destroyed or damaged beyond repair.
1945 is also the year where on Lüneburg Heath the unconditional surrender of the three German armies operating in Northwest Germany was signed. The location is presently inaccessible to the general public as it lies within a military out-of-bounds area. Only a small monument on a nearby track alludes to the event. On 23 May 1945, Reichsführer SS Heinrich Himmler took his own life in Lüneburg whilst in British Army custody by biting into a potassium cyanide capsule embedded in his teeth before he could be properly interrogated. He was subsequently buried in an unmarked location in a nearby forest.
Post-war period
[edit]Even before the Nuremberg Trials took place, the first war crimes trial, the so-called Belsen Trial (Bergen-Belsen-Prozess), began in Lüneburg on 17 September 1945 conducted against 45 former SS men, women and kapos (prisoner functionaries) from the Bergen-Belsen and Auschwitz concentration camps.
After World War II, Lüneburg became part of the new state of Lower Saxony. But the dilapidated state of its buildings led to various plans to try to improve living conditions. One proposition that was seriously discussed was to tear down the entire Altstadt and replace it with modern buildings. The ensuing public protest resulted in Lüneburg becoming the focal point for a new concept: cultural heritage conservation. Since the early 1970s the town has been systematically restored. A leading figure in this initiative since the late 1960s has been Curt Pomp: against much opposition from politicians and councillors he founded and championed the Lüneburg Altstadt Working Group (Arbeitskreis Lüneburger Altstadt) for the preservation of historic buildings. His engagement was rewarded with the German Prize for Cultural Heritage Conservation and the German Order of Merit. Today Lüneburg is a tourist attraction as a result of the restoration and important sectors of the town's economy also depend on tourism.
Between Lüneburg and Soltau to the southwest, a large military training area, the Soltau-Lüneburg Training Area (SLTA), was established by the British and Canadian military, which was used from 1963 to 1994. It was governed by the Soltau-Lüneburg Agreement between the Federal Republic of Germany, the United Kingdom and Canada. The area was located on the Lüneburg Heath and was heavily used particularly by tanks and other armoured vehicles.
The salt mine was closed in 1980, ending the thousand-year tradition of salt mining, although small amounts are still mined for ceremonial purposes. Small bags of salt may be purchased in the town hall, and bags are given as a gift from the town to all couples married in the town. After the closing of the salt mines, the town gained new relevance from its university, which was founded in 1989.
As part of the restructuring of Defence in 1990 two of the three Bundeswehr barracks in the town were closed and the remaining one reduced in size. The Bundesgrenzschutz barracks was also closed. Lüneburg University moved to the site of the old Scharnhorst barracks. The university grew out of the new economics and cultural studies departments set up in the 1980s and their amalgamation with the College of Education (Pädagogischen Hochschule or PH) that took place in 1989. Since its move to the former barracks site the university has enrolled increasing numbers of students. The expansion of the university is an important contribution to the restructuring of the town into a service centre.
Today an industrial estate, the Lünepark, has been built on the terrain of the old Bundesgrenzschutz barracks with its new industrial premises for entrepreneurs. The promotion of trade and industry has resulted in many firms from the ICT area locating themselves there. In May 2006 the nearby Johannes Westphal Bridge was opened to traffic. This links the newly created Lünepark with the suburb of Goseburg on the far side of the Ilmenau. Since 5 October 2007 Lüneburg has been able to call itself a Hanseatic Town; together with Stade it is one of only two towns in Lower Saxony to bear the title.
Amalgamated villages/communities
[edit]- 1943: Hagen and Lüne
- 1974: Häcklingen, Ochtmissen, Oedeme and Rettmer as well as the Ortsteile of Alt-Hagen, Ebensberg and Pflegerdorf/Gut Wienebüttel.
Geography
[edit]

Location
[edit]Lüneburg lies on the river Ilmenau, about 30 kilometres (19 mi) from its confluence with the Elbe. The river flows through the town and is featured in its song; it was formerly traversed by cogs taking salt from the town to the other, larger, ports of the Hanseatic League nearby.
To the south of the town stretches the 7,400-square-kilometre (2,857 sq mi) Lüneburg Heath which emerged as a result of widespread tree-felling, forest fires and grazing. The tradition that the heath arose from centuries of logging undertaken to meet the constant need of the Lüneburg salt works for wood is not historically confirmed. More likely, the heath was originally formed by clearances during the Bronze Age. The old town (Altstadt) of Lüneburg lies above a salt dome which is the town's original source of prosperity. However, the constant mining of the salt deposits over which the town stands has also resulted in the sometimes gradual, sometimes dramatically pronounced, sinking of various areas of the town. On the western edge of the town is the Kalkberg, a small hill and former gypsum quarry.
Neighbouring towns and cities
[edit]There are several towns, cities, and urban areas around Lüneburg in all directions:
| Winsen (Luhe), Hamburg-Harburg 18 km (11 mi), 36 km |
Hamburg-Bergedorf, Schwarzenbek, Lübeck 32 km (20 mi), 43 km (27 mi), 87 km (54 mi) |
Adendorf, Lauenburg 5 km (3 mi), 22 km (14 mi) |
| Jesteburg 48 km (30 mi) |

|
Amt Neuhaus, Lübtheen 42 km (26 mi), 57 km |
| Soltau 51 km (32 mi) |
Ebstorf, Uelzen 26 km (16 mi), 37 km (23 mi) |
Lüchow (Wendland) 68 km |
Town layout
[edit]Historical quarters
[edit]

The motto Mons, Pons, Fons ("Hill, bridge, spring") characterised the development of the town from the 8th century as it coalesced from initially three, and later four, areas of settlement. These areas were the refuge castle on the — at that time considerably higher — Kalkberg, together with its adjoining settlement (the Marktviertel or "Market Quarter"), the village of Modestorpe between the bridge over the river Ilmenau and the large square, Am Sande (the Sandviertel or "Sand Quarter"), and the saline with its walled settlement for the work force (the Sülzviertel or "Salt Quarter"). Not until the 13th century was the river port settlement (the Wasserviertel or "Waterside Quarter") built between the market place and the Ilmenau. The resulting shape of the town thus formed did not change until its expansion in the late 19th century and it is still clearly visible today. Lüneburg's six historic town gates were the Altenbrücker Tor, the Bardowicker Tor, the Rote Tor, the Sülztor, the Lüner Tor and the Neue Tor.
Stadtteile
[edit]Lüneburg has the following Stadtteile: Altstadt, Bockelsberg, Ebensberg, Goseburg-Zeltberg, Häcklingen, Kaltenmoor (the largest Stadtteil, with around 8,000 inhabitants), Kreideberg, Lüne, Moorfeld, Mittelfeld, Neu Hagen, Ochtmissen, Oedeme, Rettmer, Rotes Feld, Schützenplatz, Weststadt and Wilschenbruch.
Jüttkenmoor, Klosterkamp, Bülows Kamp, In den Kämpen, Krähornsberg, Schäferfeld, Volgershall and Zeltberg are the names of individual blocks within a single Stadtteil.
Subsidence
[edit]The houses in the historic quarter between the Lüneburg Saltworks (today the German Salt Museum) and the Kalkberg were built above a salt dome that was excavated by the saltworks and which extended to just below the surface of the ground. As a result of the increasing quantities of salt mined with improved technical equipment after 1830, the ground began to sink by several metres. This resulted in the so-called Senkungsgebiet or "subsidence area". The houses there and the local church (St. Lambert's) lost their stability and had to be demolished. Because of this subsidence, and because salt mining was increasingly unprofitable, the saltworks were finally closed in 1980. Today, only small amounts of brine are extracted for the health spa in the Lüneburg Thermal Salt Baths (the Salztherme Lüneburg or SaLü). One side of the saltworks now houses a supermarket, while the other is the German Salt Museum.
The subsidence has been monitored at about 240 stations since 1946 every two years. The land has not quite stopped subsiding yet, but it is stable enough that new construction has taken place on it, and several historic buildings which had previously been damaged or demolished have been restored. The subsidence can still be clearly seen even today. Those who walk from Am Sande to the end of the Grapengießerstraße can clearly sense the degree of subsidence for themselves: the hollow in front of them was formerly at the same level as the Grapengießerstraße. This depression extends as far as the Lambertiplatz square.
In the Frommestraße, another sign of earth movements caused by salt mining may be seen: the Tor zur Unterwelt ("Door to the Underworld"), where two cast iron doors have been pushed on top of one another.
Near the church St. Michaelis, other consequences of the subsidence can be seen in its sloping columns and the west wing of the nave. Current subsidence movements can be seen in the road known as Ochtmisser Kirchsteig.
Climate
[edit]Lüneburg has an oceanic climate (Köppen: Cfb; Trewartha: Dolk). The average temperature ranges from 1 °C (34 °F) in winter to 17 °C (63 °F) in summer. Precipitation is evenly distributed throughout the year, with slightly more precipitation in summer than in winter.
The Lüneburg weather station has recorded the following extreme values:[12]
- Its highest temperature was 37.2 °C (99.0 °F) on 9 August 1992.
- Its lowest temperature was −25.7 °C (−14.3 °F) on 24 February 1956.
- Its greatest annual precipitation was 836.5 mm (32.93 in) in 1954.
- Its least annual precipitation was 306.6 mm (12.07 in) in 1959.
- The longest annual sunshine was 1,861.1 hours in 1953.
- The shortest annual sunshine was 1,277.8 hours in 1962.
| Climate data for Lüneburg, 1961–1990 normals, extremes 1948–1997 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.1 (57.4) |
19.2 (66.6) |
24.0 (75.2) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.6 (87.1) |
34.4 (93.9) |
35.4 (95.7) |
37.2 (99.0) |
34.3 (93.7) |
25.6 (78.1) |
20.5 (68.9) |
16.5 (61.7) |
37.2 (99.0) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 9.0 (48.2) |
10.3 (50.5) |
15.4 (59.7) |
21.3 (70.3) |
26.1 (79.0) |
29.4 (84.9) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.4 (86.7) |
25.4 (77.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
14.4 (57.9) |
11.0 (51.8) |
31.8 (89.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
3.9 (39.0) |
7.5 (45.5) |
12.3 (54.1) |
17.6 (63.7) |
20.8 (69.4) |
21.9 (71.4) |
22.1 (71.8) |
18.4 (65.1) |
13.5 (56.3) |
7.6 (45.7) |
4.0 (39.2) |
12.7 (54.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.5 (32.9) |
1.1 (34.0) |
3.9 (39.0) |
7.6 (45.7) |
12.7 (54.9) |
15.9 (60.6) |
17.2 (63.0) |
16.9 (62.4) |
13.7 (56.7) |
9.7 (49.5) |
5.1 (41.2) |
1.9 (35.4) |
8.8 (47.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −2.2 (28.0) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
0.5 (32.9) |
3.0 (37.4) |
7.3 (45.1) |
10.5 (50.9) |
12.3 (54.1) |
12.0 (53.6) |
9.5 (49.1) |
6.2 (43.2) |
2.5 (36.5) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
4.9 (40.8) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | −11.5 (11.3) |
−10.2 (13.6) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
1.0 (33.8) |
4.8 (40.6) |
7.3 (45.1) |
6.6 (43.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
−14.8 (5.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −22.1 (−7.8) |
−25.7 (−14.3) |
−17.0 (1.4) |
−7.1 (19.2) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
1.7 (35.1) |
4.4 (39.9) |
2.5 (36.5) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−17.0 (1.4) |
−19.2 (−2.6) |
−25.7 (−14.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 46.9 (1.85) |
34.6 (1.36) |
43.8 (1.72) |
43.6 (1.72) |
53.4 (2.10) |
64.2 (2.53) |
62.9 (2.48) |
61.5 (2.42) |
54.8 (2.16) |
43.2 (1.70) |
51.2 (2.02) |
50.3 (1.98) |
610.4 (24.03) |
| Average extreme snow depth cm (inches) | 7.6 (3.0) |
8.7 (3.4) |
5.0 (2.0) |
0.5 (0.2) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1.9 (0.7) |
5.1 (2.0) |
13.9 (5.5) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 17.3 | 13.6 | 15.9 | 14.8 | 14.7 | 14.4 | 16.1 | 14.8 | 15.0 | 14.3 | 16.7 | 17.4 | 185.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 85.9 | 82.7 | 79.2 | 74.6 | 70.9 | 71.8 | 74.0 | 74.9 | 79.7 | 83.0 | 84.6 | 86.1 | 78.9 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 39.5 | 63.0 | 100.6 | 152.5 | 208.7 | 213.8 | 201.2 | 199.6 | 139.6 | 96.9 | 48.9 | 31.4 | 1,495.6 |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst / SKlima.de[12] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
[edit]Lüneburg already had about 14,000 inhabitants in the Late Middle Ages and beginning of the Modern Period and was one of the largest 'cities' of its time, but its population shrank with the economic downturn to just 9,400 in 1757; then rose again to 10,400 in 1813. With the onset of industrialisation in the 19th century, population growth accelerated. If 13,000 were living in the town in 1855, by 1939 there were as many as 35,000. Shortly after the Second World War, refugees and displaced persons from Germany's eastern territories brought an increase in population within just a few months of around 18,000 people so that the total number in December 1945 was 53,000. In 2003 the 70,000 level was exceeded for the first time.
The town of Lüneburg, its eponymous district and the neighbouring district of Harburg belong to the few regions in Germany that have experienced such a massive growth. The reasons for this include the growth of areas around the Hamburg Metropolitan Region and the consequent shift of people to those areas. The Lower Saxon State Office for Statistics has forecast that the town of Lüneburg will have a population of 89,484 by the year 2021. More realistic estimates, however, put the future size Lüneburg at between 75,000 and 79,000 in that time frame.
On 31 December 2008, according to the Statistics Office, the official census for Lüneburg recorded 72,492 people (those who had their main residence in the town and after adjustments with other states offices) – the highest number in its history. Currently Lüneburg is the eleventh largest centre of population in Lower Saxony. In addition Lüneburg has particularly close relations with its adjacent municipalities which are also growing and with which it is forming an agglomeration. The town, together with the nearby villages of Adendorf, Bardowick, Deutsch Evern, Reppenstedt, Vögelsen and Wendisch Evern, has a total population of about 103,000 and, on that basis, would qualify as a city (in Germany cities or Großstädte are defined as settlements with a population of over 100,000). The town council has the plan to extend the population by adding these villages to the town area.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1530 | 14,000 | — |
| 1699 | 11,000 | −21.4% |
| 1757 | 9,426 | −14.3% |
| 1813 | 10,400 | +10.3% |
| 1855 | 13,352 | +28.4% |
| 1861 | 14,400 | +7.8% |
| 1867 | 15,900 | +10.4% |
| 1871 | 16,284 | +2.4% |
| 1890 | 20,665 | +26.9% |
| 1900 | 24,693 | +19.5% |
| 1910 | 27,790 | +12.5% |
| 1925 | 28,923 | +4.1% |
| 1933 | 31,171 | +7.8% |
| 1939 | 35,239 | +13.1% |
| 1945 | 53,095 | +50.7% |
| 1950 | 58,139 | +9.5% |
| 1956 | 56,845 | −2.2% |
| 1961 | 59,563 | +4.8% |
| 1965 | 60,269 | +1.2% |
| 1970 | 59,516 | −1.2% |
| 1975 | 64,586 | +8.5% |
| 1980 | 62,225 | −3.7% |
| 1985 | 59,645 | −4.1% |
| 1990 | 61,870 | +3.7% |
| 2000 | 67,398 | +8.9% |
| 2010 | 71,549 | +6.2% |
| 2019 | 78,024 | +9.0% |
| Nationality | Population (2013) |
|---|---|
| 608 | |
| 438 | |
| 221 | |
| 182 | |
| 170 | |
| 141 |
The following overview shows the population figures based on the situation at the time. Up to 1813 they were mostly estimates; thereafter based on censuses (*) or official projections by the State Office of Statistics. From 1871 the figures were based on those 'present in the town', from 1925 on those 'living in the town' and since 1987 on the 'population who have their main residence in the town'. Before 1871 the numbers were based on inconsistent survey methods.
Governance
[edit]The town of Lüneburg is part of 'State Constituency 49 Lüneburg' and 'Federal Constituency No. 38 Lüchow-Dannenberg – Lüneburg'.[14][15]
Council
[edit]Local election results in 2021 for the town council of Lüneburg:[16]
Mayor
[edit]Before the Second World War the lord mayor (Oberbürgermeister) was the full-time head of the town's administration. On the introduction of the North German council constitution by the British occupation forces power was separated: the voluntary lord mayor and chairman of the town body was the political representative of the town who, like all the members of the town council was elected by the people, whilst the administration was headed up by a full-time chief municipal director, who was elected by the town council. Since 1996, as a result of the reform of the local constitution, both functions (again) have been combined in the post of a full-time lord mayor, who is now directly elected by the townsfolk. In addition to the lord mayor there are other mayors (elected by the council) who support and represent the lord mayor in his civic duties.
- 1945–1946: Werner Bockelmann, SPD
- 1946–1949: Ernst Braune, SPD
- 1949–1951: Paul Müller, DP
- 1951–1952: Erich Dieckmann, DP
- 1952–1954: Peter Gravenhorst, DP
- 1954–1955: Reinhold Kreitmeyer, FDP
- 1955–1958: Peter Gravenhorst, DP
- 1958–1961: Wilhelm Hilmer, SPD
- 1961–1964: Erich Drenckhahn, CDU
- 1964–1978: Alfred Trebchen, SPD
- 1978–1981: Heinz Schlawatzky, SPD
- 1981–1987: Horst Nickel, CDU
- 1987–1991: Jens Schreiber, CDU
- 1991–2021: Ulrich Mädge, SPD
- since 2021: Claudia Kalisch, Bündnis 90/Die Grünen
The current mayors are: Hiltrud Lotze (SPD), Jule Grunau (Bündnis 90/Die Grünen), and Christel John (CDU).
Twin towns – sister cities
[edit]In addition Lüneburg has friendly relations with German towns Kulmbach and Köthen.[17]
Sports
[edit]The Lüneburger SK Hansan football team formed when Lüneburger SK with the football section of Lüneburger SV, Oberliga.
Education
[edit]The town has one university, the Leuphana Universität Lüneburg (previously known only as the Universität Lüneburg). The university has more than 7,000 students.[18]
Transport
[edit]The town is served by Lüneburg station. The nearest airport is Hamburg Airport, located 77 km (48 mi) north west of Lüneburg.
Notable people
[edit]




Public service and thinking
[edit]- Lucas Bacmeister (1530–1608), Lutheran Theologian and church music composer
- Jacob Kroger (ca 1550–1594), court goldsmith to Anne of Denmark and thief
- Johann von Götzen (1599–1645), nobleman and Generalfeldmarschall
- Jean Armand de Lestocq (1692–1767), French adventurer, influenced the foreign policy of Russia during the early reign of Elizabeth of Russia
- Georg Freytag (1788–1861), philologist[19]
- Johanna Stegen (1793–1842), heroine of the Napoleonic Wars, she rushed ammunition to Prussian troop in her apron, thus becoming "The Heroine of Lüneburg"
- Rudolf von Bennigsen (1824–1902), politician[20]
- Charles Schroeter (1837–1921), US Army soldier who received the Medal of Honor for his actions during the American Indian Wars
- Paul von Hindenburg (1847–1934), general and statesman, honorary citizen of Lüneburg in 1918 for his service in the World War I; President of Germany from 1925 to 1934[21]
- Paul von Osterroht (1887–1917), World War I fighter pilot
- Walter Bötcher (1898–1981), Oberstadtdirektor of Lüneburg from 1955 to 1963
Arts
[edit]- Johann Georg Ebeling (1637–1676), editor and composer of hymns[22] by Paul Gerhardt
- Georg Böhm (1661–1733), organist of the St. John's Church, Lüneburg in 1698–1733
- Johann Sebastian Bach (1685–1750), attended St. Michael's School and sang in its choir 1700 to 1703[23][24]
- Johann Abraham Peter Schulz (1747–1800), composer and conductor.[25]
- Heinrich Heine (1797–1856), poet, journalist and essayist, likely to have composed his poem Lorelei here
- Eduard Krüger (1807–1885), musicologist, composer and philologist.
- Hans Winderstein (1856–1925), conductor and composer
- Charlotte Huhn (1865–1925), an operatic contralto.
- Margarete Boie (1880–1946), author, lived and died locally
- Jean Leppien (1910–1991), a German-French painter.
- Susanne Linke (born 1944), dancer and choreographer, innovator of German Tanztheater
- Annegret Soltau (born 1946), visual artist
- Mirko Reisser (born 1971), a.k.a. DAIM, graffiti artist
- Anjorka Strechel (born 1982), film and theatre actress
Science & business
[edit]- Otto Volger (1822–1897), geologist
- August Ritter (1826–1908), civil engineer, author of method to calculate for arches, bridges and roofs.[26]
- Bernhard Riemann (1826–1866), mathematician, worked on analysis, number theory and differential geometry; went to school locally
- Gustav Wallis (1830–1878), plant collector, who introduced over 1,000 plant species to Europe
- Ernst Ehlers (1835–1925), zoologist
- Louis Boehmer (1843–1896), German-American agronomist and government advisor in Meiji period Japan
- Niklas Luhmann (1927–1998), sociologist and philosopher of social science
- Detlev Ganten (born 1941), specialist in pharmacology and molecular medicine
- Detlef Franke (1952–2007), Egyptologist
Sport
[edit]- Hasso von Bismarck (1902–1941), bobsledder who competed at the 1932 Winter Olympics
- Ralf Sievers (born 1961), footballer, played over 275 games
- Hannelore Brenner (born 1963), paralympian dressage equestrian athlete
- Bahne Rabe (1963–2001), rower and gold medallist at the 1988 Summer Olympics & bronze medallist at the 1992 Summer Olympics
- Katarina Waters (born 1980), English-American professional wrestler and actress
- Anja Noske (born 1986), rower, twice world champion
- Fabian Stenzel (born 1986), footballer who has played over 310 games
- Sören Ludolph (born 1988), middle-distance runner, competed at the 2012 Summer Olympics
- John Franklin III (born 1994), American football player
Gallery
[edit]-
Am Sande
-
Am Sande
-
The nearby Lüneburg Heath is an anthropogenic heath.
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ German: [ˈlyːnəbʊʁk] ⓘ; Low German: Lümborg; Latin: Luneburgum or Lunaburgum; Old High German: Luneburc; Old Saxon: Hliuni; Polabian: Glain.
- ^ German: Hansestadt Lüneburg.
- ^ Pronounced /ˈljuːnənbɜːrɡ/ LEW-nən-burg.
References
[edit]- ^ "Stichwahlen zu Direktwahlen in Niedersachsen vom 26. September 2021" (PDF). Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen. 13 October 2021.
- ^ "Alle politisch selbständigen Gemeinden mit ausgewählten Merkmalen am 31.12.2023" (in German). Federal Statistical Office of Germany. 28 October 2024. Retrieved 16 November 2024.
- ^ "Zahlen, Daten, Fakten" [Numbers, dates and facts]. Hansestadt Lüneburg.
- ^ "What to see in Lüneburg: Most beautiful spots - Ship Me There". Ship Me There. 2021-03-19. Archived from the original on 2022-07-02. Retrieved 2025-05-31.
- ^ Vgl.: Monumenta Germaniae Historica D O1, 183
- ^ "Lueneburg". Jewish Virtual Library. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ Georg Braun (1574). "Luneburgum". Beschreibung und Contrafactur der vornembster Stät der Welt (in German and Latin). Vol. 1. Illustrator: Frans Hogenberg, Simon Novellanus. pp. 23-23a. OCLC 1042126159. OL 33146694M. Wikidata Q55360295.
- ^ "Old Salt Route". Metropolregion Hamburg. Retrieved 19 October 2025.
- ^ "Discovery of a looted estate leads to family reunion – DW – 11/20/2018". dw.com. Retrieved 2024-01-19.
- ^ "Gedenkstätte | Psychiatrische Klinik Lüneburg". www.pk.lueneburg.de. Archived from the original on 2014-05-12. Retrieved 2025-05-31.
- ^ 'Lüneburg (massacre on 11 April 1945' - KZ-Gedenkstätte Neuengamme, retrieved on June 30, 2024
- ^ a b "Monatsauswertung". sklima.de (in German). SKlima. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ "Statistik Staatsangehörigkeit - Zuständigkeitsbereich" (PDF). www.lueneburg.de. Hansestadt Lüneburg. Retrieved 2014-12-20.
- ^ "Hansestadt Lüneburg - Ergebnisse Kommunalwahl 2021". Retrieved 2025-06-03.
- ^ a b "Lüneburg und die Welt". hansestadtlueneburg.de (in German). Lüneburg. Archived from the original on 2019-04-27. Retrieved 2021-02-19.
- ^ "The University: Facts and Figures". Leuphana Universität Lüneburg. Archived from the original on 2015-09-15. Retrieved 2014-04-05.
- ^ . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 11 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 212.
- ^ . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 03 (11th ed.). 1911.
- ^ Dierich, Anne-Kathrin. "Ehrungen und Ehrenbürger Hansestadt Lüneburg". www.lueneburg.de (in German). Archived from the original on 2009-02-08. Retrieved 2025-05-31.
- ^ "DNB, Katalog der Deutschen Nationalbibliothek". portal.dnb.de. Retrieved 2025-05-31.
- ^ The New Bach Reader, p. 37
- ^ "Bach, J. S.: Lüneburg (1700–1703)". Jan.ucc.nau.edu. Retrieved 2015-10-29.
- ^ . New International Encyclopedia. Vol. XVII. 1905.
- ^ . New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
Sources
[edit] This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Leuphana". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Leuphana". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
External links
[edit]- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 17 (11th ed.). 1911.
- Official website (in German)
- Leuphana University (in German)